Report
Report
Report
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
14 QUANTIFICATION OF BENEFITS FROM ECONOMIC COOPERATION IN SOUTH ASIA<br />
1.9). This is mainly due to the free trade agreement<br />
between the two nations, its geographical proximity,<br />
free current account convertibility between its currency<br />
and Indian rupees and generous grants from India.<br />
Table 1.9 Top Export Markets of Bhutan<br />
(in Million Nu), 2000–03<br />
Countries 2000 2001 2002 2003<br />
India 4376.95 4700.47 5153.78 5188.23<br />
Bangladesh 164.72 222.38 222.97 120.83<br />
Nepal 28.44 41.51 32.79 14.19<br />
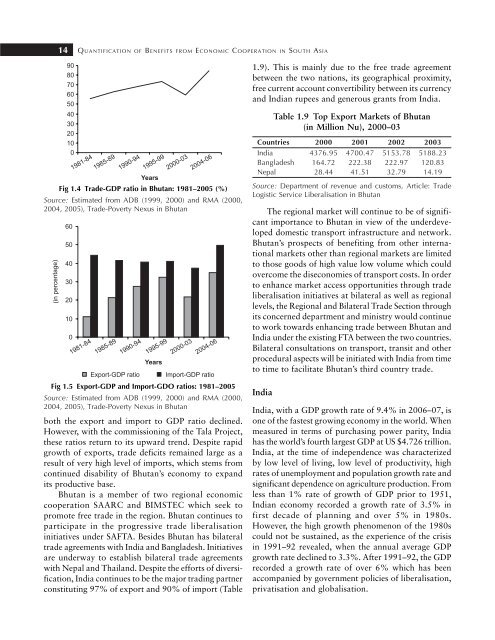
Fig 1.4 Trade-GDP ratio in Bhutan: 1981–2005 (%)<br />
Source: Estimated from ADB (1999, 2000) and RMA (2000,<br />
2004, 2005), Trade-Poverty Nexus in Bhutan<br />
Fig 1.5 Export-GDP and Import-GDO ratios: 1981–2005<br />
Source: Estimated from ADB (1999, 2000) and RMA (2000,<br />
2004, 2005), Trade-Poverty Nexus in Bhutan<br />
both the export and import to GDP ratio declined.<br />
However, with the commissioning of the Tala Project,<br />
these ratios return to its upward trend. Despite rapid<br />
growth of exports, trade deficits remained large as a<br />
result of very high level of imports, which stems from<br />
continued disability of Bhutan’s economy to expand<br />
its productive base.<br />
Bhutan is a member of two regional economic<br />
cooperation SAARC and BIMSTEC which seek to<br />
promote free trade in the region. Bhutan continues to<br />
participate in the progressive trade liberalisation<br />
initiatives under SAFTA. Besides Bhutan has bilateral<br />
trade agreements with India and Bangladesh. Initiatives<br />
are underway to establish bilateral trade agreements<br />
with Nepal and Thailand. Despite the efforts of diversification,<br />
India continues to be the major trading partner<br />
constituting 97% of export and 90% of import (Table<br />
Source: Department of revenue and customs, Article: Trade<br />
Logistic Service Liberalisation in Bhutan<br />
The regional market will continue to be of significant<br />
importance to Bhutan in view of the underdeveloped<br />
domestic transport infrastructure and network.<br />
Bhutan’s prospects of benefiting from other international<br />
markets other than regional markets are limited<br />
to those goods of high value low volume which could<br />
overcome the diseconomies of transport costs. In order<br />
to enhance market access opportunities through trade<br />
liberalisation initiatives at bilateral as well as regional<br />
levels, the Regional and Bilateral Trade Section through<br />
its concerned department and ministry would continue<br />
to work towards enhancing trade between Bhutan and<br />
India under the existing FTA between the two countries.<br />
Bilateral consultations on transport, transit and other<br />
procedural aspects will be initiated with India from time<br />
to time to facilitate Bhutan’s third country trade.<br />
India<br />
India, with a GDP growth rate of 9.4% in 2006–07, is<br />
one of the fastest growing economy in the world. When<br />
measured in terms of purchasing power parity, India<br />
has the world’s fourth largest GDP at US $4.726 trillion.<br />
India, at the time of independence was characterized<br />
by low level of living, low level of productivity, high<br />
rates of unemployment and population growth rate and<br />
significant dependence on agriculture production. From<br />
less than 1% rate of growth of GDP prior to 1951,<br />
Indian economy recorded a growth rate of 3.5% in<br />
first decade of planning and over 5% in 1980s.<br />
However, the high growth phenomenon of the 1980s<br />
could not be sustained, as the experience of the crisis<br />
in 1991–92 revealed, when the annual average GDP<br />
growth rate declined to 3.3%. After 1991–92, the GDP<br />
recorded a growth rate of over 6% which has been<br />
accompanied by government policies of liberalisation,<br />
privatisation and globalisation.