rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
52 MACROECONOMIC, TRADE, AND AID DEVELOPMENTS GLOBAL MONITORING REPORT 2013<br />
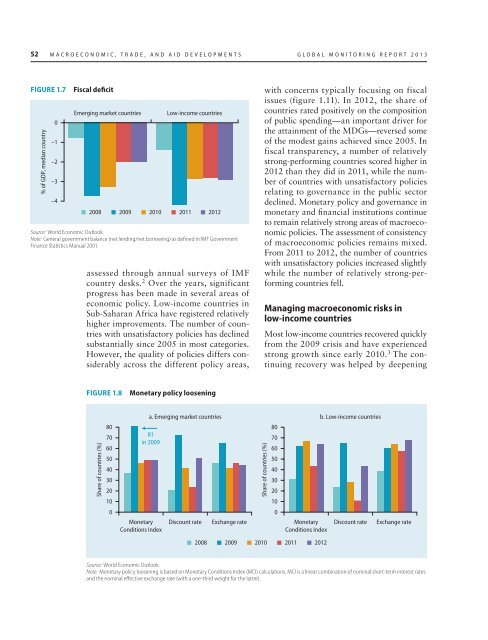
FIGURE 1.7<br />
% of GDP, median country<br />
0<br />
–1<br />
–2<br />
–3<br />
–4<br />
Fiscal deficit<br />
Emerging market countries<br />
Low-income countries<br />
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012<br />
Source: World Economic Outlook.<br />
Note: General government balance (net lending/net borrowing) as defined in IMF Government<br />
Finance Statistics Manual 2001.<br />
assessed through annual surveys of IMF<br />
country desks. 2 Over the years, significant<br />
progress has been made in several areas of<br />
economic policy. Low-income countries in<br />
Sub-Saharan Africa have registered relatively<br />
higher improvements. The number of countries<br />
with unsatisfactory policies has declined<br />
substantially since 2005 in most categories.<br />
However, the quality of policies differs considerably<br />
across the different policy areas,<br />
with concerns typically focusing on fiscal<br />
issues (figure 1.11). In 2012, the share of<br />
countries rated positively on the composition<br />
of public spending—an important driver for<br />
the attainment of the MDGs—reversed some<br />
of the modest gains achieved since 2005. In<br />
fiscal transparency, a number of relatively<br />
strong-performing countries scored higher in<br />
2012 than they did in 2011, while the number<br />
of countries with unsatisfactory policies<br />
relating to governance in the public sector<br />
declined. Monetary policy and governance in<br />
monetary and financial institutions continue<br />
to remain relatively strong areas of macroeconomic<br />
policies. The assessment of consistency<br />
of macroeconomic policies remains mixed.<br />
From 2011 to 2012, the number of countries<br />
with unsatisfactory policies increased slightly<br />
while the number of relatively strong-performing<br />
countries fell.<br />
Managing macroeconomic risks in<br />
low-income countries<br />
Most low-income countries recovered quickly<br />
from the 2009 crisis and have experienced<br />
strong growth since early 2010. 3 The continuing<br />
recovery was helped by deepening<br />
FIGURE 1.8<br />
Monetary policy loosening<br />
Share of countries (%)<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
a. Emerging market countries<br />
81<br />
in 2009<br />
Share of countries (%)<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
b. Low-income countries<br />
0<br />
Monetary<br />
Conditions Index<br />
Discount rate<br />
Exchange rate<br />
0<br />
Monetary<br />
Conditions Index<br />
Discount rate<br />
Exchange rate<br />
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012<br />
Source: World Economic Outlook.<br />
Note: Monetary policy loosening is based on Monetary Conditions Index (MCI) calculations. MCI is a linear combination of nominal short-term interest rates<br />
and the nominal effective exchange rate (with a one-third weight for the latter).