rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
rural-urban dynamics_report.pdf - Khazar University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
GLOBAL MONITORING REPORT 2013 MACROECONOMIC, TRADE, AND AID DEVELOPMENTS 53<br />
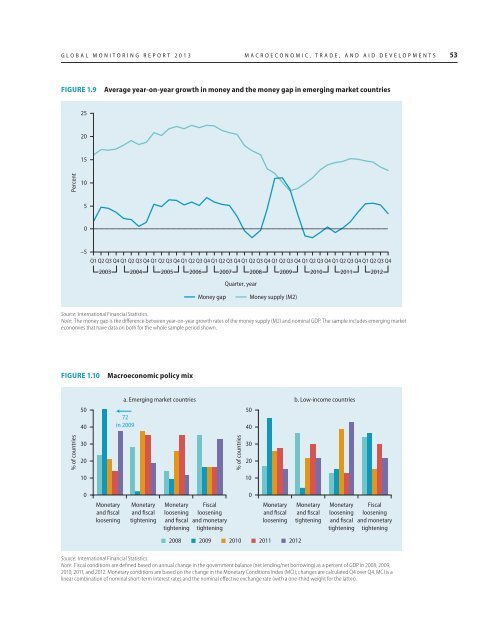
FIGURE 1.9<br />
Average year-on-year growth in money and the money gap in emerging market countries<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
Percent<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
–5<br />
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4<br />
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012<br />
Quarter, year<br />
Money gap<br />
Money supply (M2)<br />
Source: International Financial Statistics.<br />
Note: The money gap is the difference between year-on-year growth rates of the money supply (M2) and nominal GDP. The sample includes emerging market<br />
economies that have data on both for the whole sample period shown.<br />
FIGURE 1.10<br />
Macroeconomic policy mix<br />
50<br />
40<br />
a. Emerging market countries<br />
72<br />
in 2009<br />
50<br />
40<br />
b. Low-income countries<br />
% of countries<br />
30<br />
20<br />
% of countries<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
10<br />
0<br />
Monetary<br />
and fiscal<br />
loosening<br />
Monetary<br />
and fiscal<br />
tightening<br />
Monetary Fiscal<br />
loosening loosening<br />
and fiscal and monetary<br />
tightening tightening<br />
0<br />
Monetary<br />
and fiscal<br />
loosening<br />
Monetary<br />
and fiscal<br />
tightening<br />
Monetary Fiscal<br />
loosening loosening<br />
and fiscal and monetary<br />
tightening tightening<br />
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012<br />
Source: International Financial Statistics.<br />
Note: Fiscal conditions are defined based on annual change in the government balance (net lending/net borrowing) as a percent of GDP in 2008, 2009,<br />
2010, 2011, and 2012. Monetary conditions are based on the change in the Monetary Conditions Index (MCI); changes are calculated Q4 over Q4. MCI is a<br />
linear combination of nominal short-term interest rates and the nominal effective exchange rate (with a one-third weight for the latter).