influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
95<br />
80 -,<br />
70 l<br />
DAvai<strong>la</strong>ble<br />
.Used<br />
60 -1<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30 ~<br />
20 J<br />
10 J<br />
o +1--'---<br />
Tœe Shrub He~<br />
'--- ------v---- ~<br />
Mean cover (%)<br />
Aspen Fruit Deci<strong>du</strong>ous Cedar Coniferous<br />
'-- ~<br />
----v-<br />
Dominant tree (%)<br />
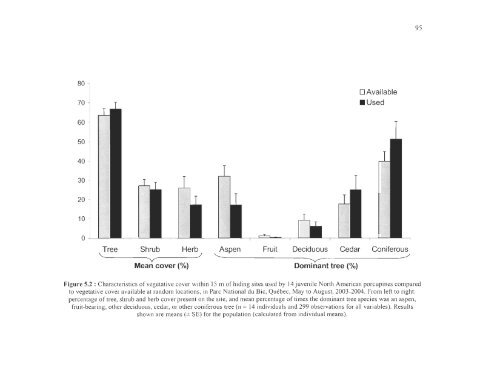
Figure 5.2: Characteristi cs of veg<strong>et</strong>ative co ver within 15 m ofhiding sites used by 14 juvenile North American porcupines compared<br />
to veg<strong>et</strong>ative co ver avai<strong>la</strong>ble at random locations, in Parc Nati onal <strong>du</strong> Bic, Québec, May to August, 2003-2004. From left to right:<br />
percentage of tree, shrub and herb cover present on the site, and mean percentage of times the dominant tree species was an aspen,<br />
fruit-bearing, other <strong>de</strong>ci<strong>du</strong>ous, cedar, or other coni fe rous tree (n = 14 indivi<strong>du</strong>als and 299 observations for al! vari ables). Results<br />
shown are means (± SE) for the popu <strong>la</strong>tion (calcul ated from indi vi<strong>du</strong>al means).