influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
influence du climat et de la prédation sur l'utilisation de l'habitat et la ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
46<br />
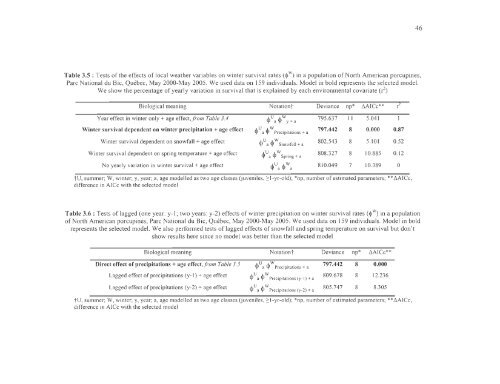
Table 3.5: Tests of the effects oflocal weather vari abl es on wi nter <strong>sur</strong>vival rates (w) in a popu<strong>la</strong>ti on of North American porcupines,<br />
Parc National <strong>du</strong> Bic, Québec, May 2000-May 2005. We used data on 159 indi vi<strong>du</strong>als. Mo<strong>de</strong>l in bold represents the selected mo<strong>de</strong>!.<br />
We show the percentage ofyearl y variati on in sUl'v ival that is exp<strong>la</strong>i ned by each environmental covari ate (r 2 )<br />
Biological meaning<br />
Year effect in winter only + age effect,F om Tab le 3.4<br />
Winter <strong>sur</strong>vival <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt on win ter precipitation + age effect<br />
Winter <strong>sur</strong>v ival <strong>de</strong> pen<strong>de</strong> nt on snowfall + age effect<br />
Winter <strong>sur</strong>vival <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt on spring temperature + age effect<br />
No yearly variation in winter <strong>sur</strong>vival + age effect<br />
Notationî Deviance np* t.AICc**<br />
U a<br />
w a<br />
810.049 7 10.389<br />
Ua w y + a<br />
795 .637 Il 5.041<br />
U a W Precipitations + a 797.442 8 0.000<br />
U a W Snowfall + a 802.543 8 5.10 1<br />
U a W Spring + a 808 .327 8 10.885<br />
r 2<br />
0.87<br />
0.52<br />
0.12<br />
0<br />
î U, summer; W, winter; y, year; a, age mo<strong>de</strong>lled as two age cl asses (juveniles, 2: 1-yr-old); *np, number of estimated param<strong>et</strong>ers; ** t.AICc,<br />
di fference in AICc with the selected mo<strong>de</strong>l<br />
Table 3.6: Tests of<strong>la</strong>gged (one year: y-l ; two years: y-2) effects ofwinter precipitation on winter <strong>sur</strong>vival rates (w) in a popu<strong>la</strong>tion<br />
of North American porcupines, Parc National <strong>du</strong> Bic, Québec, May 2000-May 2005. We used data on 159 indivi<strong>du</strong>als. Mo<strong>de</strong>l in bold<br />
represents the selected mo<strong>de</strong>!. We also performed tests of <strong>la</strong>gged effects of snowfa ll and spring temperature on <strong>sur</strong>viva! but don't<br />
show resu!ts here since no mo<strong>de</strong>l was b<strong>et</strong>ter than the se!ected mo<strong>de</strong>l<br />
Biological meaning Notati onî Deviance np* t.AICc* *<br />
Direct effect of precipitations + age effect,Fom Table 3.5<br />
U W<br />
a Precipitations + a<br />
797.442 8 0.000<br />
Lagged effect of precipitations (y-I ) + age effect ua W Precipi ta tions (y_l) + a 809.678 8 12.236<br />
Lagged effect of precipitations (y-2) + age effect U a W Precipitations (y-2) + a<br />
805 .747 8 8.305<br />
îU, summer; W, winter; y, year; a, age mo<strong>de</strong>lled as two age c<strong>la</strong>sses (j uven il es, 2: 1-yr-old); *np, number of estimated param<strong>et</strong>ers; ** t.AICc,<br />
di fference in AICc with the selected mo<strong>de</strong>l