ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<str<strong>on</strong>g>ABSTRACTS</str<strong>on</strong>g> FROM 17 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON <strong>CRRT</strong>,<br />
SAN DIEGO, FEB 14-17, 2012<br />
p-RIFLE at 72hrs allow to predict<br />
mortality at PICU.<br />
36. Creatinine Producti<strong>on</strong> and<br />
Creatinine Degradati<strong>on</strong> are<br />
Reduce in Patients with Acute<br />
Kidney Injury and Sepsis<br />
Rolando Claure-Del Granado, Josee<br />
Bouchard, Shar<strong>on</strong> Soroko, Glenn M<br />
Chertow, J<strong>on</strong>athan Himmelfarb, Alp T<br />
Ikizler, Emil P Paganini, Ravindra L<br />
Mehta<br />
University of California San Diego,<br />
University of M<strong>on</strong>treal, Stanford<br />
University, University of Washingt<strong>on</strong>,<br />
Vanderbilt University, Cleveland Clinic<br />
Background: Diagnosis and staging of<br />
acute kidney injury (AKI) uses serum<br />
creatinine (sCr). In a previous animal<br />
model of AKI, Doi et al have shown that<br />
sepsis dramatically decreases sCr levels<br />
and creatinine producti<strong>on</strong>. This<br />
phenomen<strong>on</strong> would limit early detecti<strong>on</strong><br />
of acute kidney injury. We evaluated the<br />
effect of sepsis <strong>on</strong> sCr levels, creatinine<br />
producti<strong>on</strong> (Pc’), and creatinine<br />
degradati<strong>on</strong> (Dc’) in patients with AKI.<br />
We hypothesized that sepsis will reduce<br />
creatinine producti<strong>on</strong> and sCr levels in<br />
AKI patients with sepsis.<br />
Methods: We analyzed data <str<strong>on</strong>g>from</str<strong>on</strong>g> 234<br />
critically ill n<strong>on</strong>-dialyzed patients with<br />
AKI <str<strong>on</strong>g>from</str<strong>on</strong>g> 5 centers included in the<br />
PICARD study. Creatinine producti<strong>on</strong><br />
was calculated using Cockcroft-Gault<br />
formula and using Moran et al formula<br />
which adjusts sCr for fluid balance.<br />
Creatinine degradati<strong>on</strong> was computed<br />
using Mitch et al equati<strong>on</strong> and adjusted<br />
for fluid balance. Results: Of the 234<br />
patients 139 were septic (59%). N<strong>on</strong>adjusted<br />
and adjusted sCr levels were<br />
lower in AKI patients with sepsis than in<br />
n<strong>on</strong>-septic patients (n<strong>on</strong>-adjusted sCr<br />
median 2. IQR [1.5 – 2.8] vs. 2.5 IQR<br />
[1.8 – 3.5] and adjusted sCr 2. IQR [1.4<br />
– 2.7] vs 2.4 IQR [1.8 – 3.6]; p < .1). Pc’<br />
was lower in septic patients than in n<strong>on</strong>septic<br />
(1,211 IQR [934 – 1,472] vs.<br />
1,278 IQR [1.17 – 1,538] mg/day; p <<br />
.1); the same was observed after<br />
adjusting Pc’ for fluid balance (1,92 IQR<br />
[828 – 1,295] vs. 1,124 IQR [892 –<br />
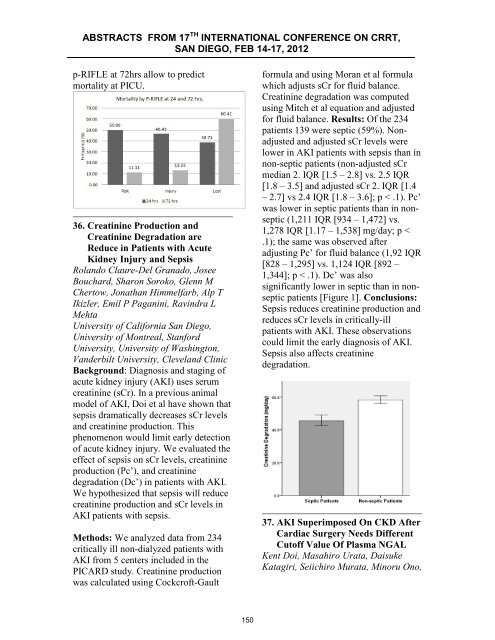
1,344]; p < .1). Dc’ was also<br />
significantly lower in septic than in n<strong>on</strong>septic<br />
patients [Figure 1]. C<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong>s:<br />
Sepsis reduces creatinine producti<strong>on</strong> and<br />
reduces sCr levels in critically-ill<br />
patients with AKI. These observati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
could limit the early diagnosis of AKI.<br />
Sepsis also affects creatinine<br />
degradati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
37. AKI Superimposed On CKD After<br />
Cardiac Surgery Needs Different<br />
Cutoff Value Of Plasma NGAL<br />
Kent Doi, Masahiro Urata, Daisuke<br />
Katagiri, Seiichiro Murata, Minoru Ono,<br />
150