ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
ABSTRACTS from 16th International COnference on ... - CRRT Online
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<str<strong>on</strong>g>ABSTRACTS</str<strong>on</strong>g> FROM 17 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON <strong>CRRT</strong>,<br />
SAN DIEGO, FEB 14-17, 2012<br />
Naoki Yahagi, Toshiro Fujita, Eisei<br />
Noiri<br />
University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan,<br />
Itabashi Chuo Medical Center, Tokyo,<br />
Japan<br />
Background: Plasma neutrophil<br />
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL)<br />
is reportedly useful for pediatric and<br />
adult post-cardiac surgery acute kidney<br />
injury (AKI). However, although chr<strong>on</strong>ic<br />
kidney disease (CKD) is a str<strong>on</strong>g risk<br />
factor for AKI development, previous<br />
clinical evaluati<strong>on</strong>s did not specifically<br />
examined AKI occurring in patients with<br />
CKD. Moreover, CKD significantly<br />
increases plasma NGAL levels in a<br />
stable c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>. Methods: This study<br />
prospectively evaluated 143 adult<br />
patients who had cardiac surgery at two<br />
general hospitals. Plasma NGAL was<br />
measured before surgery, at ICU arrival<br />
after the surgery ( hr), and 2, 4, 12, 24,<br />
36, 6 hr after ICU arrival. Results:<br />
Based <strong>on</strong> patients’ estimated glomerular<br />
filtrati<strong>on</strong> rate (GFR) before surgery, 67<br />
(46.9%) were diagnosed as having CKD.<br />
Of 143 patients, 54 (37.8%) developed<br />
AKI after surgery. Multiple logistic<br />
regressi<strong>on</strong> analysis revealed that<br />
preoperative estimated GFR and<br />
operati<strong>on</strong> time were significantly<br />
associated with AKI occurrence after<br />
surgery. Plasma NGAL measured before<br />
surgery and at , 2, 4, 12, 24, and 36 hr<br />
after ICU arrival in AKI was<br />
significantly higher than in n<strong>on</strong>-AKI<br />
regardless of CKD complicati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
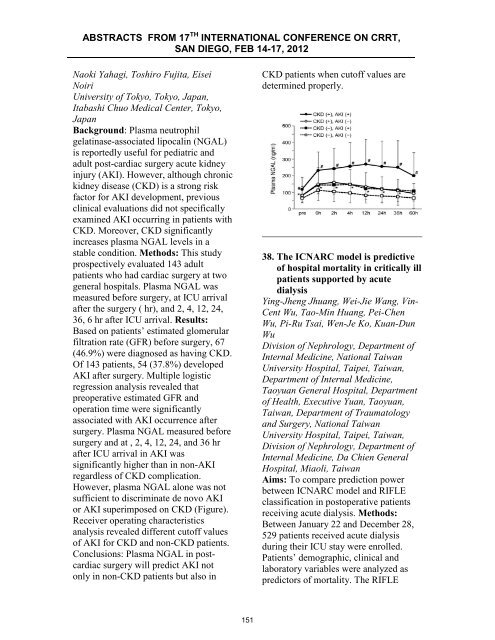
However, plasma NGAL al<strong>on</strong>e was not<br />
sufficient to discriminate de novo AKI<br />
or AKI superimposed <strong>on</strong> CKD (Figure).<br />
Receiver operating characteristics<br />
analysis revealed different cutoff values<br />
of AKI for CKD and n<strong>on</strong>-CKD patients.<br />
C<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong>s: Plasma NGAL in postcardiac<br />
surgery will predict AKI not<br />
<strong>on</strong>ly in n<strong>on</strong>-CKD patients but also in<br />
CKD patients when cutoff values are<br />
determined properly.<br />
38. The ICNARC model is predictive<br />
of hospital mortality in critically ill<br />
patients supported by acute<br />
dialysis<br />
Ying-Jheng Jhuang, Wei-Jie Wang, Vin-<br />
Cent Wu, Tao-Min Huang, Pei-Chen<br />
Wu, Pi-Ru Tsai, Wen-Je Ko, Kuan-Dun<br />
Wu<br />
Divisi<strong>on</strong> of Nephrology, Department of<br />
Internal Medicine, Nati<strong>on</strong>al Taiwan<br />
University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan,<br />
Department of Internal Medicine,<br />
Taoyuan General Hospital, Department<br />
of Health, Executive Yuan, Taoyuan,<br />
Taiwan, Department of Traumatology<br />
and Surgery, Nati<strong>on</strong>al Taiwan<br />
University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan,<br />
Divisi<strong>on</strong> of Nephrology, Department of<br />
Internal Medicine, Da Chien General<br />
Hospital, Miaoli, Taiwan<br />
Aims: To compare predicti<strong>on</strong> power<br />
between ICNARC model and RIFLE<br />
classificati<strong>on</strong> in postoperative patients<br />
receiving acute dialysis. Methods:<br />
Between January 22 and December 28,<br />
529 patients received acute dialysis<br />
during their ICU stay were enrolled.<br />
Patients’ demographic, clinical and<br />
laboratory variables were analyzed as<br />
predictors of mortality. The RIFLE<br />
151