Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
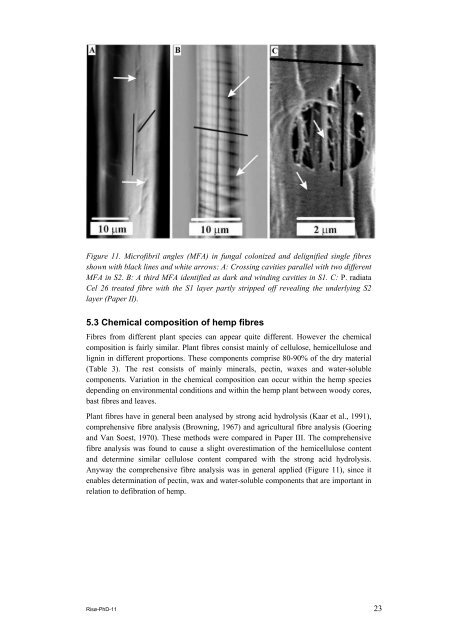
Figure 11. Micr<strong>of</strong>ibril angles (MFA) in fungal colonized and delignified single <strong>fibre</strong>s<br />
shown with black lines and white arrows: A: Crossing cavities parallel with two different<br />
MFA in S2. B: A third MFA identified as dark and winding cavities in S1. C: P. radiata<br />
Cel 26 treated <strong>fibre</strong> with the S1 layer partly stripped <strong>of</strong>f revealing the underlying S2<br />
layer (Paper II).<br />
5.3 Chemical composition <strong>of</strong> <strong>hemp</strong> <strong>fibre</strong>s<br />
Fibres from different plant species can appear quite different. However the chemical<br />
composition is fairly similar. Plant <strong>fibre</strong>s consist mainly <strong>of</strong> cellulose, hemicellulose and<br />
lignin in different proportions. These components comprise 80-90% <strong>of</strong> the dry material<br />
(Table 3). The rest consists <strong>of</strong> mainly minerals, pectin, waxes and water-soluble<br />
components. Variation in the chemical composition can occur within the <strong>hemp</strong> species<br />
depending on environmental conditions and within the <strong>hemp</strong> plant between woody cores,<br />
bast <strong>fibre</strong>s and leaves.<br />
Plant <strong>fibre</strong>s have in general been analysed by strong acid hydrolysis (Kaar et al., 1991),<br />
comprehensive <strong>fibre</strong> analysis (Browning, 1967) and agricultural <strong>fibre</strong> analysis (Goering<br />
and Van Soest, 1970). These methods were compared in Paper III. The comprehensive<br />
<strong>fibre</strong> analysis was found to cause a slight overestimation <strong>of</strong> the hemicellulose content<br />
and determine similar cellulose content compared with the strong acid hydrolysis.<br />
<strong>An</strong>yway the comprehensive <strong>fibre</strong> analysis was in general applied (Figure 11), since it<br />
enables determination <strong>of</strong> pectin, wax and water-soluble components that are important in<br />
relation to defibration <strong>of</strong> <strong>hemp</strong>.<br />
Risø-PhD-11 23