Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Table 4. The plant <strong>fibre</strong>s cellulose crystallinity, calculated by Rietveld refinement, (g/100<br />
g cellulose) and chemical composition measured by comprehensive <strong>fibre</strong> analysis (g/100<br />
g dry matter) (Paper III and IV).<br />
Material<br />
Cellulose Cellulose Sample Amorphous Residual<br />
crystallinity<br />
crystallity cellulose components<br />
g/100 g cellu. g/100 g DM g/100 g DM g/100 g DM g/100 g DM<br />
Hemp <strong>fibre</strong>s 94 64 60 4 36<br />
Norway spruce 67 49 33 16 51<br />
Barley straw 100 43 43 0 57<br />
Corn stover 100 33 33 0 67<br />
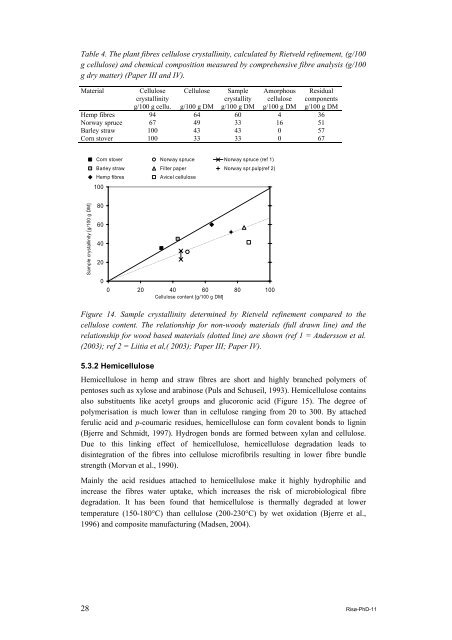
Sample crystallinity [g/100 g DM] ...<br />
Corn stover Norway spruce Norway spruce (ref 1)<br />
Barley straw Filter paper Norway spr.pulp(ref 2)<br />
Hemp <strong>fibre</strong>s Avicel cellulose<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100<br />
Cellulose content [g/100 g DM]<br />
Figure 14. Sample crystallinity determined by Rietveld refinement compared to the<br />
cellulose content. The relationship for non-woody materials (full drawn line) and the<br />
relationship for wood based materials (dotted line) are shown (ref 1 = <strong>An</strong>dersson et al.<br />
(2003); ref 2 = Liitia et al,( 2003); Paper III; Paper IV).<br />
5.3.2 Hemicellulose<br />
Hemicellulose in <strong>hemp</strong> and straw <strong>fibre</strong>s are short and highly branched <strong>polymer</strong>s <strong>of</strong><br />
pentoses such as xylose and arabinose (Puls and Schuseil, 1993). Hemicellulose contains<br />
also substituents like acetyl groups and glucoronic acid (Figure 15). The degree <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>polymer</strong>isation is much lower than in cellulose ranging from 20 to 300. By attached<br />
ferulic acid and p-coumaric residues, hemicellulose can form covalent bonds to lignin<br />
(Bjerre and Schmidt, 1997). Hydrogen bonds are formed between xylan and cellulose.<br />
Due to this linking effect <strong>of</strong> hemicellulose, hemicellulose degradation leads to<br />
disintegration <strong>of</strong> the <strong>fibre</strong>s into cellulose micr<strong>of</strong>ibrils resulting in lower <strong>fibre</strong> bundle<br />
strength (Morvan et al., 1990).<br />
Mainly the acid residues attached to hemicellulose make it highly hydrophilic and<br />
increase the <strong>fibre</strong>s water uptake, which increases the risk <strong>of</strong> microbiological <strong>fibre</strong><br />
degradation. It has been found that hemicellulose is thermally degraded at lower<br />
temperature (150-180°C) than cellulose (200-230°C) by wet oxidation (Bjerre et al.,<br />
1996) and composite manufacturing (Madsen, 2004).<br />
28 Risø-PhD-11