Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Properties of hemp fibre polymer composites -An optimisation of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
9 Composites reinforced with <strong>hemp</strong> <strong>fibre</strong>s<br />
9.1 Effect <strong>of</strong> <strong>fibre</strong> orientation on mechanical properties<br />
Plant <strong>fibre</strong> reinforced <strong>composites</strong> are generally made with randomly orientated <strong>fibre</strong>s or<br />
aligned <strong>fibre</strong>s. Composites with aligned <strong>fibre</strong>s are generally stronger and stiffer in the<br />
<strong>fibre</strong> direction than <strong>composites</strong> with randomly orientated <strong>fibre</strong>s.<br />
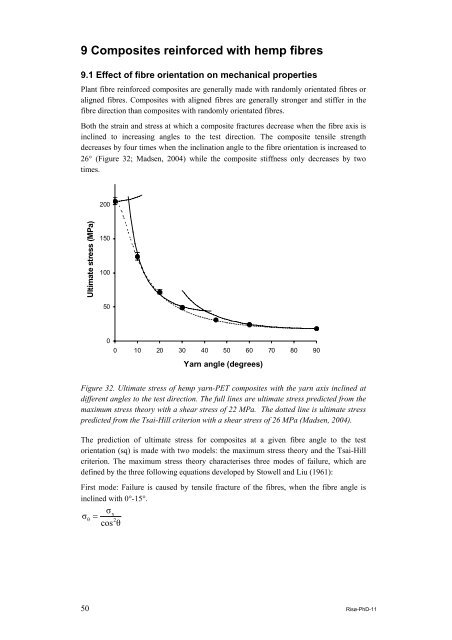
Both the strain and stress at which a composite fractures decrease when the <strong>fibre</strong> axis is<br />
inclined to increasing angles to the test direction. The composite tensile strength<br />
decreases by four times when the inclination angle to the <strong>fibre</strong> orientation is increased to<br />
26° (Figure 32; Madsen, 2004) while the composite stiffness only decreases by two<br />
times.<br />
Ultimate stress (MPa)<br />
200<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90<br />
Yarn angle (degrees)<br />
Figure 32. Ultimate stress <strong>of</strong> <strong>hemp</strong> yarn-PET <strong>composites</strong> with the yarn axis inclined at<br />
different angles to the test direction. The full lines are ultimate stress predicted from the<br />
maximum stress theory with a shear stress <strong>of</strong> 22 MPa. The dotted line is ultimate stress<br />
predicted from the Tsai-Hill criterion with a shear stress <strong>of</strong> 26 MPa (Madsen, 2004).<br />
The prediction <strong>of</strong> ultimate stress for <strong>composites</strong> at a given <strong>fibre</strong> angle to the test<br />
orientation (sq) is made with two models: the maximum stress theory and the Tsai-Hill<br />
criterion. The maximum stress theory characterises three modes <strong>of</strong> failure, which are<br />
defined by the three following equations developed by Stowell and Liu (1961):<br />
First mode: Failure is caused by tensile fracture <strong>of</strong> the <strong>fibre</strong>s, when the <strong>fibre</strong> angle is<br />
inclined with 0°-15°.<br />
σx<br />
σθ 2<br />
cos θ<br />
=<br />
50 Risø-PhD-11