NUI Galway – UL Alliance First Annual ENGINEERING AND - ARAN ...
NUI Galway – UL Alliance First Annual ENGINEERING AND - ARAN ...
NUI Galway – UL Alliance First Annual ENGINEERING AND - ARAN ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Dwelling Energy Measurement Procedure<br />
Brendan E. Hoare and Colm V. Cryan PhD.<br />
Civil Engineering and Material Science department<br />
University of Limerick<br />
Brendan.Hoare@ul.ie<br />
Abstract<br />
Abstract <strong>–</strong> This study presents a building energy<br />
measurement procedure utilising a Zigbee wireless<br />
sensor network. It is presented as an alternative to the<br />
Dwelling Energy Assessment Procedure (DEAP)<br />
yielding the actual energy performance of the building.<br />
The procedure not only takes the design and materials<br />
used into account, but also the standards of<br />
workmanship and current maintenance condition.<br />
1. Introduction<br />
The dwelling energy assessment procedure<br />
(DEAP) is encapsulated in Irish law as the method used<br />
to assess the energy performance of a residential<br />
building. The owner of every building that is sold or<br />
leased is required to provide a building energy rating<br />
(BER) certificate. The BER is calculated by DEAP<br />
based on the design, location and material specifications<br />
of the building. Important parameters such as<br />
workmanship and maintenance condition, which<br />
significantly impact performance, are not considered.<br />
Recent advances in wireless sensor networks<br />
(WSN’s) have enabled the development of noninvasive,<br />
distributed sensor systems. Such systems can<br />
gather data from a large number of nodes and<br />
communicate the information back to a central hub for<br />
analysis. The aim of this project is to explore the use of<br />
such a system to measure the actual thermal<br />
performance of a building: the Dwelling Energy<br />
Measurement Procedure (DEMP.)<br />
An important output of the project is the<br />
determination of a figure of merit for the building that<br />
equates to its actual thermal performance; in a manner<br />
similar to the BER. In addition, it is intended that the<br />
system will allow users to see how the thermal<br />
performance varies from room to room: something<br />
which DEAP does not facilitate.<br />
Having reviewed the hardware and software<br />
requirements for the system and considered a range of<br />
options; the Zigbee standard was selected for this study.<br />
2. Zigbee Standard<br />
Zigbee (IEEE 802.15.4) is an emerging wireless<br />
technology standard, developed by the Zigbee <strong>Alliance</strong>.<br />
The standard is designed to facilitate the provision of<br />
low-cost, low power, personal area networks. The<br />
standard can support up to 65,000 nodes, operating at<br />
up to 250 kbps. In this study star and mesh network<br />
topologies are being explored and the capabilities and<br />
suitability of each is being assessed.<br />
19<br />
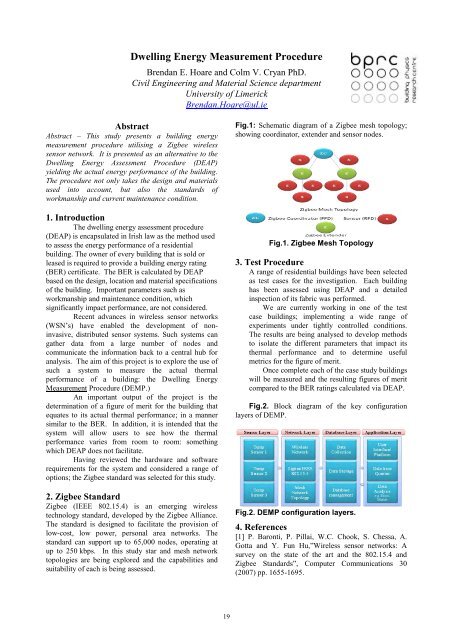
Fig.1: Schematic diagram of a Zigbee mesh topology;<br />
showing coordinator, extender and sensor nodes.<br />
Fig.1. Zigbee Mesh Topology<br />
3. Test Procedure<br />
A range of residential buildings have been selected<br />
as test cases for the investigation. Each building<br />
has been assessed using DEAP and a detailed<br />
inspection of its fabric was performed.<br />
We are currently working in one of the test<br />
case buildings; implementing a wide range of<br />
experiments under tightly controlled conditions.<br />
The results are being analysed to develop methods<br />
to isolate the different parameters that impact its<br />
thermal performance and to determine useful<br />
metrics for the figure of merit.<br />
Once complete each of the case study buildings<br />
will be measured and the resulting figures of merit<br />
compared to the BER ratings calculated via DEAP.<br />
Fig.2. Block diagram of the key configuration<br />
layers of DEMP.<br />
Fig.2. DEMP configuration layers.<br />
4. References<br />
[1] P. Baronti, P. Pillai, W.C. Chook, S. Chessa, A.<br />
Gotta and Y. Fun Hu,”Wireless sensor networks: A<br />
survey on the state of the art and the 802.15.4 and<br />
Zigbee Standards”, Computer Communications 30<br />
(2007) pp. 1655-1695.