5. Commands and Functions - Sanyo Denki America, Inc.
5. Commands and Functions - Sanyo Denki America, Inc.
5. Commands and Functions - Sanyo Denki America, Inc.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
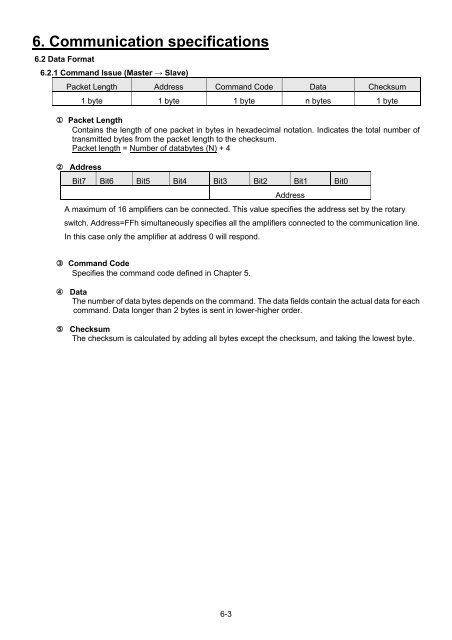
6. Communication specifications<br />
6.2 Data Format<br />
6.2.1 Comm<strong>and</strong> Issue (Master → Slave)<br />
Packet Length Address Comm<strong>and</strong> Code Data Checksum<br />
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte n bytes 1 byte<br />
Packet Length<br />
Contains the length of one packet in bytes in hexadecimal notation. Indicates the total number of<br />
transmitted bytes from the packet length to the checksum.<br />
Packet length = Number of databytes (N) + 4<br />
Address<br />
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0<br />
Address<br />
A maximum of 16 amplifiers can be connected. This value specifies the address set by the rotary<br />
switch. Address=FFh simultaneously specifies all the amplifiers connected to the communication line.<br />
In this case only the amplifier at address 0 will respond.<br />
Comm<strong>and</strong> Code<br />
Specifies the comm<strong>and</strong> code defined in Chapter <strong>5.</strong><br />
Data<br />
The number of data bytes depends on the comm<strong>and</strong>. The data fields contain the actual data for each<br />
comm<strong>and</strong>. Data longer than 2 bytes is sent in lower-higher order.<br />
Checksum<br />
The checksum is calculated by adding all bytes except the checksum, <strong>and</strong> taking the lowest byte.<br />
6-3