The Implementation of a Model of Person-Centred Practice In Older ...
The Implementation of a Model of Person-Centred Practice In Older ...
The Implementation of a Model of Person-Centred Practice In Older ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>The</strong> implementation <strong>of</strong> a model <strong>of</strong> person-centred practice in older person settings<br />
the end <strong>of</strong> the programme but with the benefit <strong>of</strong> hindsight would be beneficial to use<br />
from the beginning <strong>of</strong> facilitation work as an evaluation method and a learning tool.<br />
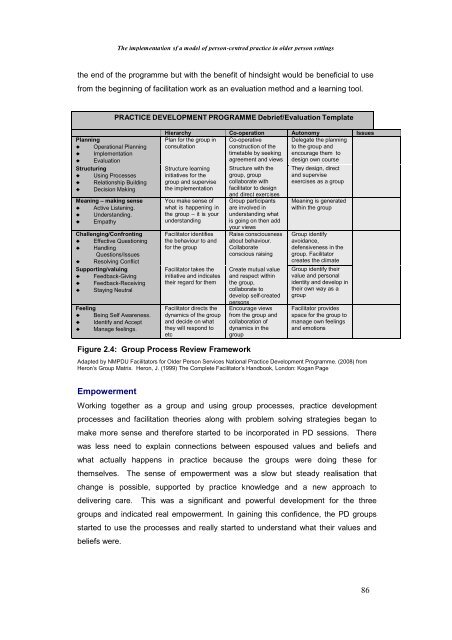
PRACTICE DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME Debrief/Evaluation Template<br />
Planning<br />
♦ Operational Planning<br />
♦ <strong>Implementation</strong><br />
♦ Evaluation<br />
Structuring<br />
♦ Using Processes<br />
♦ Relationship Building<br />
♦ Decision Making<br />
Meaning – making sense<br />
♦ Active Listening.<br />
♦ Understanding.<br />
♦ Empathy<br />
Challenging/Confronting<br />
♦ Effective Questioning<br />
♦ Handling<br />
Questions/Issues<br />
♦ Resolving Conflict<br />
Supporting/valuing<br />
♦ Feedback-Giving<br />
♦ Feedback-Receiving<br />
♦ Staying Neutral<br />
Feeling<br />
♦ Being Self Awareness.<br />
♦ Identify and Accept<br />
♦ Manage feelings.<br />
Hierarchy Co-operation Autonomy Issues<br />
Plan for the group in<br />
consultation<br />
Structure learning<br />
initiatives for the<br />
group and supervise<br />
the implementation<br />
You make sense <strong>of</strong><br />
what is happening in<br />
the group – it is your<br />
understanding<br />
Facilitator identifies<br />
the behaviour to and<br />
for the group<br />
Facilitator takes the<br />
initiative and indicates<br />
their regard for them<br />
Facilitator directs the<br />
dynamics <strong>of</strong> the group<br />
and decide on what<br />
they will respond to<br />
etc<br />
Co-operative<br />
construction <strong>of</strong> the<br />
timetable by seeking<br />
agreement and views<br />
Structure with the<br />
group, group<br />
collaborate with<br />
facilitator to design<br />
and direct exercises<br />
Group participants<br />
are involved in<br />
understanding what<br />
is going on then add<br />
your views<br />
Raise consciousness<br />
about behaviour.<br />
Collaborate<br />
conscious raising<br />
Create mutual value<br />
and respect within<br />
the group,<br />
collaborate to<br />
develop self-created<br />
persons<br />
Encourage views<br />
from the group and<br />
collaboration <strong>of</strong><br />
dynamics in the<br />
group<br />
Delegate the planning<br />
to the group and<br />
encourage them to<br />
design own course<br />
<strong>The</strong>y design, direct<br />
and supervise<br />
exercises as a group<br />
Meaning is generated<br />
within the group<br />
Group identify<br />
avoidance,<br />
defensiveness in the<br />
group. Facilitator<br />
creates the climate<br />
Group identify their<br />
value and personal<br />
identity and develop in<br />
their own way as a<br />
group<br />
Facilitator provides<br />
space for the group to<br />
manage own feelings<br />
and emotions<br />
Figure 2.4: Group Process Review Framework<br />
Adapted by NMPDU Facilitators for <strong>Older</strong> <strong>Person</strong> Services National <strong>Practice</strong> Development Programme. (2008) from<br />
Heron’s Group Matrix. Heron, J. (1999) <strong>The</strong> Complete Facilitator’s Handbook, London: Kogan Page<br />
Empowerment<br />
Working together as a group and using group processes, practice development<br />
processes and facilitation theories along with problem solving strategies began to<br />
make more sense and therefore started to be incorporated in PD sessions. <strong>The</strong>re<br />
was less need to explain connections between espoused values and beliefs and<br />
what actually happens in practice because the groups were doing these for<br />
themselves. <strong>The</strong> sense <strong>of</strong> empowerment was a slow but steady realisation that<br />
change is possible, supported by practice knowledge and a new approach to<br />
delivering care. This was a significant and powerful development for the three<br />
groups and indicated real empowerment. <strong>In</strong> gaining this confidence, the PD groups<br />
started to use the processes and really started to understand what their values and<br />
beliefs were.<br />
86