Conducting a Participatory Situation Analysis of.pdf - Global HIV ...
Conducting a Participatory Situation Analysis of.pdf - Global HIV ...
Conducting a Participatory Situation Analysis of.pdf - Global HIV ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Combination <strong>of</strong> Quantitative and<br />
Qualitative Methods<br />
Using both quantitative and qualitative methods<br />
<strong>of</strong>fers a more detailed and meaningful description <strong>of</strong><br />
the situation <strong>of</strong> orphans and vulnerable children than<br />
using only one method. Qualitative information can<br />
guide the crafting <strong>of</strong> survey questions and be used to<br />
help interpret the causes and meanings <strong>of</strong> statistical<br />
findings.As illustrated in the following example, using<br />
only quantitative data might lead to a recommendation<br />
for getting more children into the existing<br />
school system. However, with the added perspective<br />
gained from focus groups, it appears that the school<br />
system itself needs an intervention before it can<br />
take in more children.<br />
Combining Quantitative and Qualitative<br />
Methods<br />
Quantitative Method (Survey)<br />
Question:Are you currently attending school?<br />
Response: 60% <strong>of</strong> boys said “yes” and 15% <strong>of</strong> girls<br />
said “yes”<br />
Qualitative Method (Focus Groups with Girls)<br />
Question:What are the reasons for not attending<br />
school? Responses:<br />
• I didn’t learn anything.<br />
• Teachers force sex on girls.<br />
• Teachers don’t care about girls learning.<br />
• Boys tease the girls and want sex.<br />
• My teacher gave me “the sickness. I’m too ill to<br />
go now.”<br />
methods also serves as a cross-check on findings and conclusions<br />
<strong>of</strong>fered by each method. In addition, using both quantitative<br />
and qualitative methods:<br />
• Avoids the possibility that the situation analysis findings<br />
are an artifact <strong>of</strong> a single method, a single<br />
source, or a single researcher’s biases<br />
• Offers a descriptive analysis <strong>of</strong> the situation as well as<br />
conveys the magnitude <strong>of</strong> the problems<br />
• Provides a way to consistently track programs over<br />
time and/or across locations<br />
• Presents compelling evidence needed to mobilize and<br />
target resources<br />
I. <strong>Analysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> Secondary Data<br />
What is it and why is it used?<br />
Analyzing secondary data involves reviewing variables in<br />
existing quantitative data sets and determining if analysis<br />
<strong>of</strong> any <strong>of</strong> the variables will inform the situation analysis<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>HIV</strong>/AIDS-affected children. For example, using the<br />
Haiti DHS data set for 2000 it is possible to produce the<br />
summary data on orphan status by type (below).<br />
Reviewing secondary data sources can significantly<br />
reduce the amount <strong>of</strong> time and effort required to gather<br />
primary data. That is, existing data sources may provide<br />
sufficient information to define the problem or terms <strong>of</strong><br />
reference for the situation analysis. A summary report <strong>of</strong><br />
secondary data analysis combined with guideline materials,<br />
such as A Framework for the Protection, Care and<br />
Support <strong>of</strong> Orphans and Vulnerable Children Living<br />
in a World with <strong>HIV</strong>/AIDS, can indicate information<br />
gaps. Primary data collection for the situation analysis<br />
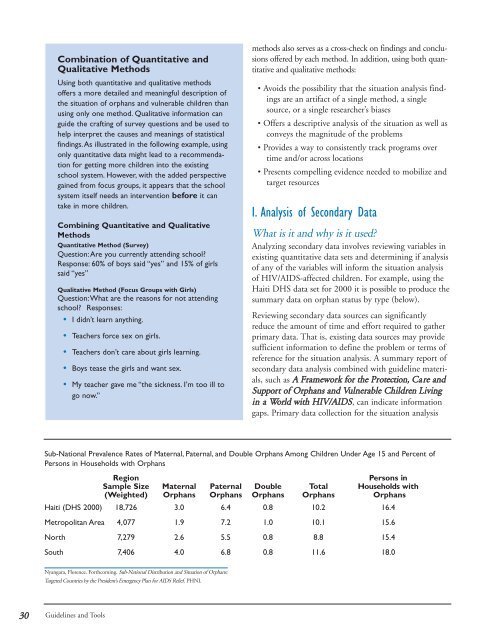
Sub-National Prevalence Rates <strong>of</strong> Maternal, Paternal, and Double Orphans Among Children Under Age 15 and Percent <strong>of</strong><br />
Persons in Households with Orphans<br />
Region<br />
Persons in<br />
Sample Size Maternal Paternal Double Total Households with<br />
(Weighted) Orphans Orphans Orphans Orphans Orphans<br />
Haiti (DHS 2000) 18,726 3.0 6.4 0.8 10.2 16.4<br />
Metropolitan Area 4,077 1.9 7.2 1.0 10.1 15.6<br />
North 7,279 2.6 5.5 0.8 8.8 15.4<br />
South 7,406 4.0 6.8 0.8 11.6 18.0<br />
Nyangara, Florence. Forthcoming. Sub-National Distribution and <strong>Situation</strong> <strong>of</strong> Orphans:<br />
Targeted Countries by the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief. PHNI.<br />
30<br />
Guidelines and Tools