PAD - LGED
PAD - LGED
PAD - LGED
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Imrprovement<br />
Total/weighted average 321.1 62% 1,796 5.8 169% 58%<br />
Note: EIRR, NPV, NPV per unit of financial cost and switching values for increased cost and decreased benefits are weighted by<br />
number of km expect for GCMs that is computed as a simple average. The last row presents average figures weighted by<br />
financial cost.<br />
B. Technical<br />
56. The project builds on the civil works components implemented under RTIP-I.<br />
Furthermore, two components, dredging of rural waterways and performance based maintenance<br />
contracts, were added for a holistic network connectivity approach and a strategic shift towards<br />
maintenance. The typical design and specification documents and cost analysis reports have been<br />
prepared for all civil work project components and are available as background documents. It<br />
will provide the standards that will be followed while preparing bill of quantities and bid<br />
documents. The basis for the average unit capital costs for the project were based on the recent<br />
biddings and contract rates for <strong>LGED</strong> projects implemented and inflated to mid-2012 values. The<br />
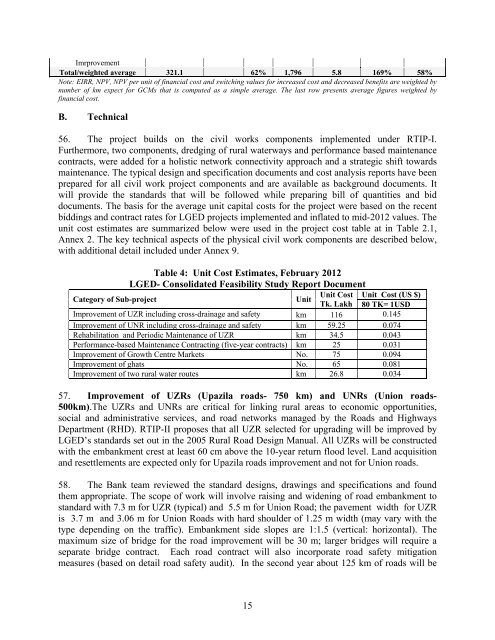
unit cost estimates are summarized below were used in the project cost table at in Table 2.1,<br />
Annex 2. The key technical aspects of the physical civil work components are described below,<br />
with additional detail included under Annex 9.<br />
Table 4: Unit Cost Estimates, February 2012<br />
<strong>LGED</strong>- Consolidated Feasibility Study Report Document<br />
Category of Sub-project<br />
Unit<br />
Unit Cost Unit Cost (US $)<br />
Tk. Lakh 80 TK= 1USD<br />
Improvement of UZR including cross-drainage and safety km 116 0.145<br />
Improvement of UNR including cross-drainage and safety km 59.25 0.074<br />
Rehabilitation and Periodic Maintenance of UZR km 34.5 0.043<br />
Performance-based Maintenance Contracting (five-year contracts) km 25 0.031<br />
Improvement of Growth Centre Markets No. 75 0.094<br />
Improvement of ghats No. 65 0.081<br />
Improvement of two rural water routes km 26.8 0.034<br />
57. Improvement of UZRs (Upazila roads- 750 km) and UNRs (Union roads-<br />
500km).The UZRs and UNRs are critical for linking rural areas to economic opportunities,<br />
social and administrative services, and road networks managed by the Roads and Highways<br />
Department (RHD). RTIP-II proposes that all UZR selected for upgrading will be improved by<br />
<strong>LGED</strong>’s standards set out in the 2005 Rural Road Design Manual. All UZRs will be constructed<br />
with the embankment crest at least 60 cm above the 10-year return flood level. Land acquisition<br />
and resettlements are expected only for Upazila roads improvement and not for Union roads.<br />
58. The Bank team reviewed the standard designs, drawings and specifications and found<br />
them appropriate. The scope of work will involve raising and widening of road embankment to<br />
standard with 7.3 m for UZR (typical) and 5.5 m for Union Road; the pavement width for UZR<br />
is 3.7 m and 3.06 m for Union Roads with hard shoulder of 1.25 m width (may vary with the<br />
type depending on the traffic). Embankment side slopes are 1:1.5 (vertical: horizontal). The<br />
maximum size of bridge for the road improvement will be 30 m; larger bridges will require a<br />
separate bridge contract. Each road contract will also incorporate road safety mitigation<br />
measures (based on detail road safety audit). In the second year about 125 km of roads will be<br />
15