eWON General Reference Guide - eWON wiki
eWON General Reference Guide - eWON wiki
eWON General Reference Guide - eWON wiki
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5.11 MEM IO Server<br />
5.11.1 Introduction<br />
<strong>General</strong> <strong>Reference</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> IO Servers Configuration<br />
The MEMORY IO Server is not a real IO server because values do not come from a peripheral. Memory Tags (Tags defined with the MEM IO<br />
server) are rather sorts of variables that can be modified by a user input or by a BASIC application. These Tags are very useful for combining<br />
different Tags and consider the result as an actual Tag i.e. having data logging capabilities and alarm management capabilities like for all other<br />
Tags.<br />
5.11.2 Setup<br />
There is no setup for the MEM <strong>eWON</strong> IO server.<br />
5.11.3 Tag name convention<br />
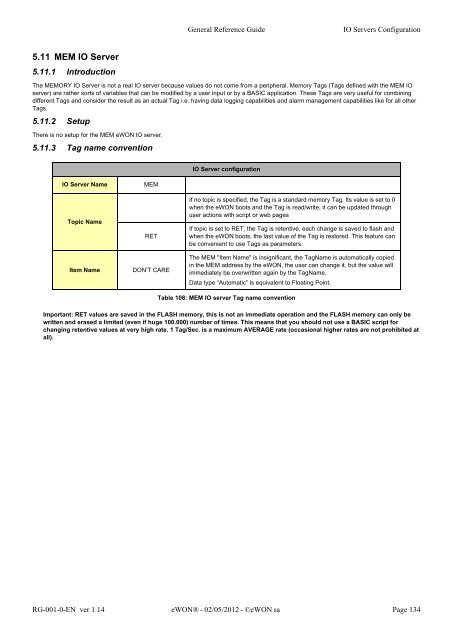
IO Server Name MEM<br />
Topic Name<br />
RET<br />
Item Name DON’T CARE<br />
IO Server configuration<br />
If no topic is specified, the Tag is a standard memory Tag. Its value is set to 0<br />
when the <strong>eWON</strong> boots and the Tag is read/write, it can be updated through<br />
user actions with script or web pages<br />
If topic is set to RET, the Tag is retentive, each change is saved to flash and<br />
when the <strong>eWON</strong> boots, the last value of the Tag is restored. This feature can<br />
be convenient to use Tags as parameters.<br />
The MEM "Item Name" is insignificant, the TagName is automatically copied<br />
in the MEM address by the <strong>eWON</strong>, the user can change it, but the value will<br />
immediately be overwritten again by the TagName.<br />
Data type “Automatic” is equivalent to Floating Point.<br />
Table 108: MEM IO server Tag name convention<br />
Important: RET values are saved in the FLASH memory, this is not an immediate operation and the FLASH memory can only be<br />
written and erased a limited (even if huge 100.000) number of times. This means that you should not use a BASIC script for<br />
changing retentive values at very high rate. 1 Tag/Sec. is a maximum AVERAGE rate (occasional higher rates are not prohibited at<br />
all).<br />
RG-001-0-EN ver 1.14 <strong>eWON</strong>® - 02/05/2012 - ©<strong>eWON</strong> sa Page 134