Workshop proceeding - final.pdf - Faculty of Information and ...
Workshop proceeding - final.pdf - Faculty of Information and ...
Workshop proceeding - final.pdf - Faculty of Information and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
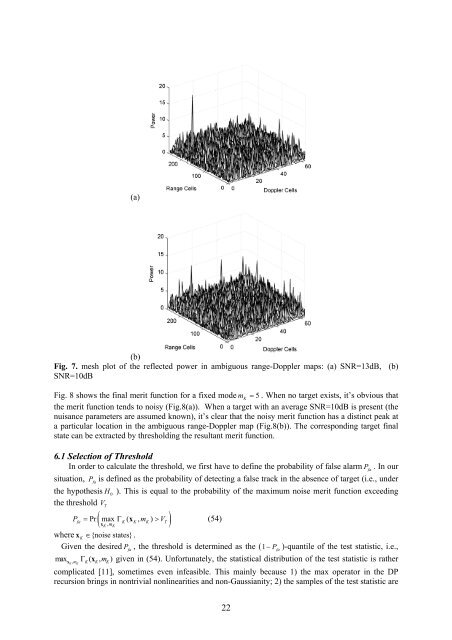
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Fig. 7. mesh plot <strong>of</strong> the reflected power in ambiguous range-Doppler maps: (a) SNR=13dB, (b)<br />
SNR=10dB<br />
Fig. 8 shows the <strong>final</strong> merit function for a fixed mode m<br />
K<br />
= 5 . When no target exists, it’s obvious that<br />
the merit function tends to noisy (Fig.8(a)). When a target with an average SNR=10dB is present (the<br />
nuisance parameters are assumed known), it’s clear that the noisy merit function has a distinct peak at<br />
a particular location in the ambiguous range-Doppler map (Fig.8(b)). The corresponding target <strong>final</strong><br />
state can be extracted by thresholding the resultant merit function.<br />
6.1 Selection <strong>of</strong> Threshold<br />
In order to calculate the threshold, we first have to define the probability <strong>of</strong> false alarm P fa<br />
. In our<br />
situation, Pfa<br />
is defined as the probability <strong>of</strong> detecting a false track in the absence <strong>of</strong> target (i.e., under<br />
the hypothesis H<br />
0<br />
). This is equal to the probability <strong>of</strong> the maximum noise merit function exceeding<br />
the threshold VT<br />
P<br />
fa<br />
= Pr ( max Γ<br />
K<br />
(<br />
K<br />
, mK ) ><br />
T<br />
xK,<br />
mK<br />
x V ) (54)<br />
where x K<br />
∈{noise states} .<br />
Given the desired P fa<br />
, the threshold is determined as the (1−<br />
Pfa<br />
)-quantile <strong>of</strong> the test statistic, i.e.,<br />
max<br />
x ,<br />
( , ) given in<br />
K m<br />
Γ<br />
K K<br />
x<br />
K<br />
mK<br />
(54). Unfortunately, the statistical distribution <strong>of</strong> the test statistic is rather<br />
complicated [11], sometimes even infeasible. This mainly because 1) the max operator in the DP<br />
recursion brings in nontrivial nonlinearities <strong>and</strong> non-Gaussianity; 2) the samples <strong>of</strong> the test statistic are<br />
22