learning-styles
learning-styles
learning-styles
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
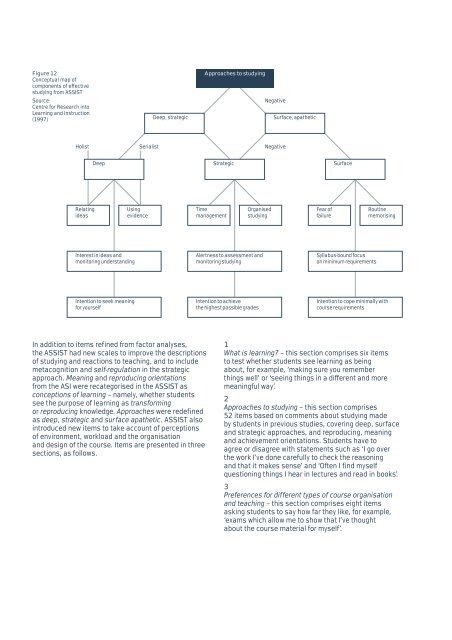
Figure 12<br />
Conceptual map of<br />
components of effective<br />
studying from ASSIST<br />
Source:<br />
Centre for Research into<br />
Learning and Instruction<br />
(1997)<br />
Deep, strategic<br />
Approaches to studying<br />
Negative<br />
Surface, apathetic<br />
Holist<br />
Serialist<br />
Negative<br />
Deep<br />
Strategic<br />
Surface<br />
Relating<br />
ideas<br />
Using<br />
evidence<br />
Time<br />
management<br />
Organised<br />
studying<br />
Fear of<br />
failure<br />
Routine<br />
memorising<br />
Interest in ideas and<br />
monitoring understanding<br />
Alertness to assessment and<br />
monitoring studying<br />
Syllabus-bound focus<br />
on minimum requirements<br />
Intention to seek meaning<br />
for yourself<br />
Intention to achieve<br />
the highest possible grades<br />
Intention to cope minimally with<br />
course requirements<br />
In addition to items refined from factor analyses,<br />
the ASSIST had new scales to improve the descriptions<br />
of studying and reactions to teaching, and to include<br />
metacognition and self-regulation in the strategic<br />
approach. Meaning and reproducing orientations<br />
from the ASI were recategorised in the ASSIST as<br />
conceptions of <strong>learning</strong> – namely, whether students<br />
see the purpose of <strong>learning</strong> as transforming<br />
or reproducing knowledge. Approaches were redefined<br />
as deep, strategic and surface apathetic. ASSIST also<br />
introduced new items to take account of perceptions<br />
of environment, workload and the organisation<br />
and design of the course. Items are presented in three<br />
sections, as follows.<br />
1<br />
What is <strong>learning</strong>? – this section comprises six items<br />
to test whether students see <strong>learning</strong> as being<br />
about, for example, ‘making sure you remember<br />
things well’ or ‘seeing things in a different and more<br />
meaningful way’.<br />
2<br />
Approaches to studying – this section comprises<br />
52 items based on comments about studying made<br />
by students in previous studies, covering deep, surface<br />
and strategic approaches, and reproducing, meaning<br />
and achievement orientations. Students have to<br />
agree or disagree with statements such as ‘I go over<br />
the work I’ve done carefully to check the reasoning<br />
and that it makes sense’ and ‘Often I find myself<br />
questioning things I hear in lectures and read in books’.<br />
3<br />
Preferences for different types of course organisation<br />
and teaching – this section comprises eight items<br />
asking students to say how far they like, for example,<br />
‘exams which allow me to show that I’ve thought<br />
about the course material for myself’.