learning-styles
learning-styles
learning-styles
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
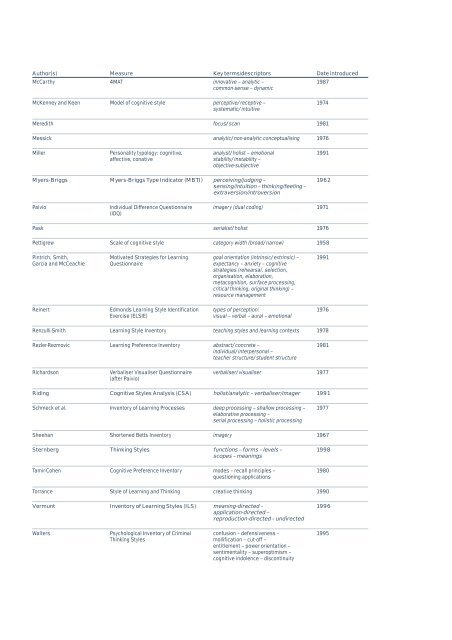
Author(s)<br />
McCarthy<br />
Measure<br />
4MAT<br />
Key terms/descriptors<br />
innovative – analytic –<br />
common-sense – dynamic<br />
Date introduced<br />
1987<br />
McKenney and Keen<br />
Model of cognitive style<br />
perceptive/receptive –<br />
systematic/intuitive<br />
1974<br />
Meredith<br />
focus/scan<br />
1981<br />
Messick<br />
analytic/non-analytic conceptualising<br />
1976<br />
Miller<br />
Personality typology: cognitive,<br />
affective, conative<br />
analyst/holist – emotional<br />
stability/instability –<br />
objective-subjective<br />
1991<br />
Myers-Briggs<br />
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)<br />
perceiving/judging –<br />
sensing/intuition – thinking/feeling –<br />
extraversion/introversion<br />
1962<br />
Paivio<br />
Individual Difference Questionnaire<br />
(IDQ)<br />
imagery (dual coding)<br />
1971<br />
Pask<br />
serialist/holist<br />
1976<br />
Pettigrew<br />
Scale of cognitive style<br />
category width (broad/narrow)<br />
1958<br />
Pintrich, Smith,<br />
Garcia and McCeachie<br />
Motivated Strategies for Learning<br />
Questionnaire<br />
goal orientation (intrinsic/extrinsic) –<br />
expectancy – anxiety – cognitive<br />
strategies (rehearsal, selection,<br />
organisation, elaboration,<br />
metacognition, surface processing,<br />
critical thinking, original thinking) –<br />
resource management<br />
1991<br />
Reinert<br />
Edmonds Learning Style Identification<br />
Exercise (ELSIE)<br />
types of perception:<br />
visual – verbal – aural – emotional<br />
1976<br />
Renzulli-Smith<br />
Learning Style Inventory<br />
teaching <strong>styles</strong> and <strong>learning</strong> contexts<br />
1978<br />
Rezler-Rezmovic<br />
Learning Preference Inventory<br />
abstract/concrete –<br />
individual/interpersonal –<br />
teacher structure/student structure<br />
1981<br />
Richardson<br />
Verbaliser Visualiser Questionnaire<br />
(after Paivio)<br />
verbaliser/visualiser<br />
1977<br />
Riding<br />
Cognitive Styles Analysis (CSA)<br />
holist/analytic – verbaliser/imager<br />
1991<br />
Schmeck et al.<br />
Inventory of Learning Processes<br />
deep processing – shallow processing –<br />
elaborative processing –<br />
serial processing – holistic processing<br />
1977<br />
Sheehan<br />
Shortened Betts Inventory<br />
imagery<br />
1967<br />
Sternberg<br />
Thinking Styles<br />
functions – forms – levels –<br />
scopes – meanings<br />
1998<br />
Tamir-Cohen<br />
Cognitive Preference Inventory<br />
modes – recall principles –<br />
questioning applications<br />
1980<br />
Torrance<br />
Style of Learning and Thinking<br />
creative thinking<br />
1990<br />
Vermunt<br />
Inventory of Learning Styles (ILS)<br />
meaning-directed –<br />
application-directed –<br />
reproduction-directed – undirected<br />
1996<br />
Walters<br />
Psychological Inventory of Criminal<br />
Thinking Styles<br />
confusion – defensiveness –<br />
mollification – cut-off –<br />
entitlement – power orientation –<br />
sentimentality – superoptimism –<br />
cognitive indolence – discontinuity<br />
1995