learning-styles
learning-styles
learning-styles
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
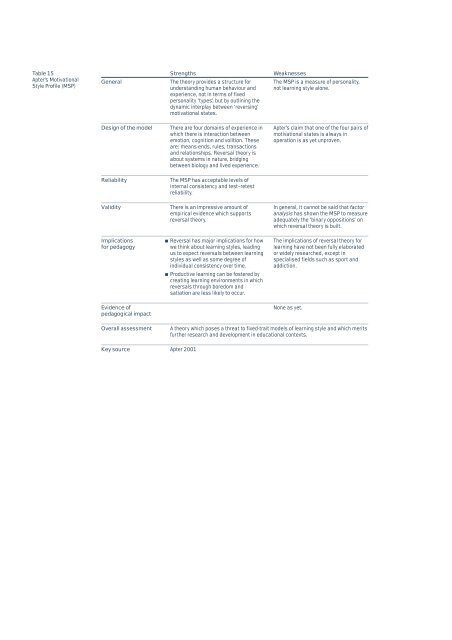
Table 15<br />
Apter’s Motivational<br />
Style Profile (MSP)<br />
General<br />
Strengths<br />
The theory provides a structure for<br />
understanding human behaviour and<br />
experience, not in terms of fixed<br />
personality ‘types’, but by outlining the<br />
dynamic interplay between ‘reversing’<br />
motivational states.<br />
Weaknesses<br />
The MSP is a measure of personality,<br />
not <strong>learning</strong> style alone.<br />
Design of the model<br />
There are four domains of experience in<br />
which there is interaction between<br />
emotion, cognition and volition. These<br />
are: means-ends, rules, transactions<br />
and relationships. Reversal theory is<br />
about systems in nature, bridging<br />
between biology and lived experience.<br />
Apter’s claim that one of the four pairs of<br />
motivational states is always in<br />
operation is as yet unproven.<br />
Reliability<br />
The MSP has acceptable levels of<br />
internal consistency and test–retest<br />
reliability.<br />
Validity<br />
There is an impressive amount of<br />
empirical evidence which supports<br />
reversal theory.<br />
In general, it cannot be said that factor<br />
analysis has shown the MSP to measure<br />
adequately the ‘binary oppositions’ on<br />
which reversal theory is built.<br />
Implications<br />
for pedagogy<br />
Reversal has major implications for how<br />
we think about <strong>learning</strong> <strong>styles</strong>, leading<br />
us to expect reversals between <strong>learning</strong><br />
<strong>styles</strong> as well as some degree of<br />
individual consistency over time.<br />
Productive <strong>learning</strong> can be fostered by<br />
creating <strong>learning</strong> environments in which<br />
reversals through boredom and<br />
satiation are less likely to occur.<br />
The implications of reversal theory for<br />
<strong>learning</strong> have not been fully elaborated<br />
or widely researched, except in<br />
specialised fields such as sport and<br />
addiction.<br />
Evidence of<br />
pedagogical impact<br />
None as yet.<br />
Overall assessment<br />
Key source<br />
A theory which poses a threat to fixed-trait models of <strong>learning</strong> style and which merits<br />
further research and development in educational contexts.<br />
Apter 2001