learning-styles
learning-styles
learning-styles
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
LSRC reference<br />
page 166/167<br />
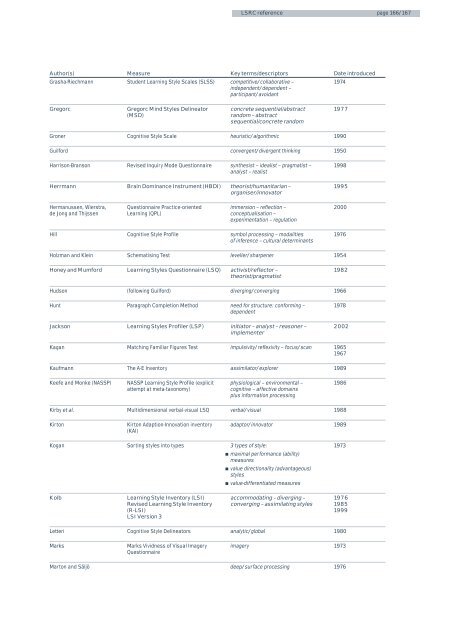
Author(s)<br />
Grasha-Riechmann<br />
Measure<br />
Student Learning Style Scales (SLSS)<br />
Key terms/descriptors<br />
competitive/collaborative –<br />
independent/dependent –<br />
participant/avoidant<br />
Date introduced<br />
1974<br />
Gregorc<br />
Gregorc Mind Styles Delineator<br />
(MSD)<br />
concrete sequential/abstract<br />
random – abstract<br />
sequential/concrete random<br />
1977<br />
Groner<br />
Cognitive Style Scale<br />
heuristic/algorithmic<br />
1990<br />
Guilford<br />
convergent/divergent thinking<br />
1950<br />
Harrison-Branson<br />
Revised Inquiry Mode Questionnaire<br />
synthesist – idealist – pragmatist –<br />
analyst – realist<br />
1998<br />
Herrmann<br />
Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI)<br />
theorist/humanitarian –<br />
organiser/innovator<br />
1995<br />
Hermanussen, Wierstra,<br />
de Jong and Thijssen<br />
Questionnaire Practice-oriented<br />
Learning (QPL)<br />
immersion – reflection –<br />
conceptualisation –<br />
experimentation – regulation<br />
2000<br />
Hill<br />
Cognitive Style Profile<br />
symbol processing – modalities<br />
of inference – cultural determinants<br />
1976<br />
Holzman and Klein<br />
Schematising Test<br />
leveller/sharpener<br />
1954<br />
Honey and Mumford<br />
Learning Styles Questionnaire (LSQ)<br />
activist/reflector –<br />
theorist/pragmatist<br />
1982<br />
Hudson<br />
(following Guilford)<br />
diverging/converging<br />
1966<br />
Hunt<br />
Paragraph Completion Method<br />
need for structure: conforming –<br />
dependent<br />
1978<br />
Jackson<br />
Learning Styles Profiler (LSP)<br />
initiator – analyst – reasoner –<br />
implementer<br />
2002<br />
Kagan<br />
Matching Familiar Figures Test<br />
impulsivity/reflexivity – focus/scan<br />
1965<br />
1967<br />
Kaufmann<br />
The A-E Inventory<br />
assimilator/explorer<br />
1989<br />
Keefe and Monke (NASSP)<br />
NASSP Learning Style Profile (explicit<br />
attempt at meta-taxonomy)<br />
physiological – environmental –<br />
cognitive – affective domains<br />
plus information processing<br />
1986<br />
Kirby et al.<br />
Multidimensional verbal-visual LSQ<br />
verbal/visual<br />
1988<br />
Kirton<br />
Kirton Adaption-Innovation inventory<br />
(KAI)<br />
adaptor/innovator<br />
1989<br />
Kogan<br />
Sorting <strong>styles</strong> into types<br />
3 types of style:<br />
maximal performance (ability)<br />
measures<br />
value directionality (advantageous)<br />
<strong>styles</strong><br />
value-differentiated measures<br />
1973<br />
Kolb<br />
Learning Style Inventory (LSI)<br />
Revised Learning Style Inventory<br />
(R-LSI)<br />
LSI Version 3<br />
accommodating – diverging –<br />
converging – assimilating <strong>styles</strong><br />
1976<br />
1985<br />
1999<br />
Letteri<br />
Cognitive Style Delineators<br />
analytic/global<br />
1980<br />
Marks<br />
Marks Vividness of Visual Imagery<br />
Questionnaire<br />
imagery<br />
1973<br />
Marton and Säljö<br />
deep/surface processing<br />
1976