DI-770 Oscilloscope provides five virtual instruments in one
DI-770 Oscilloscope provides five virtual instruments in one
DI-770 Oscilloscope provides five virtual instruments in one
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>DI</strong>-<strong>770</strong> and WINDAQ/Scope Manual<br />
The orig<strong>in</strong>al signal is sampled at a sample time t. The critical frequency (Nyquist frequency) is (1/2t) Hz.<br />
W<strong>in</strong>dow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
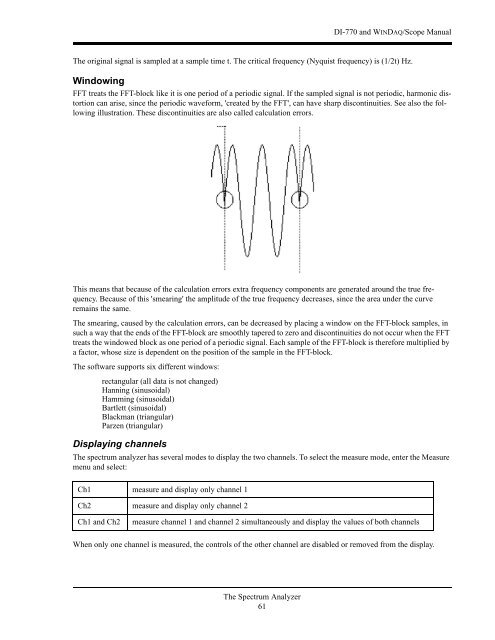
FFT treats the FFT-block like it is <strong>one</strong> period of a periodic signal. If the sampled signal is not periodic, harmonic distortion<br />
can arise, s<strong>in</strong>ce the periodic waveform, 'created by the FFT', can have sharp discont<strong>in</strong>uities. See also the follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
illustration. These discont<strong>in</strong>uities are also called calculation errors.<br />
This means that because of the calculation errors extra frequency comp<strong>one</strong>nts are generated around the true frequency.<br />
Because of this 'smear<strong>in</strong>g' the amplitude of the true frequency decreases, s<strong>in</strong>ce the area under the curve<br />
rema<strong>in</strong>s the same.<br />
The smear<strong>in</strong>g, caused by the calculation errors, can be decreased by plac<strong>in</strong>g a w<strong>in</strong>dow on the FFT-block samples, <strong>in</strong><br />
such a way that the ends of the FFT-block are smoothly tapered to zero and discont<strong>in</strong>uities do not occur when the FFT<br />
treats the w<strong>in</strong>dowed block as <strong>one</strong> period of a periodic signal. Each sample of the FFT-block is therefore multiplied by<br />
a factor, whose size is dependent on the position of the sample <strong>in</strong> the FFT-block.<br />
The software supports six different w<strong>in</strong>dows:<br />
rectangular (all data is not changed)<br />
Hann<strong>in</strong>g (s<strong>in</strong>usoidal)<br />
Hamm<strong>in</strong>g (s<strong>in</strong>usoidal)<br />
Bartlett (s<strong>in</strong>usoidal)<br />
Blackman (triangular)<br />
Parzen (triangular)<br />
Display<strong>in</strong>g channels<br />
The spectrum analyzer has several modes to display the two channels. To select the measure mode, enter the Measure<br />
menu and select:<br />
Ch1 measure and display only channel 1<br />
Ch2 measure and display only channel 2<br />
Ch1 and Ch2<br />
measure channel 1 and channel 2 simultaneously and display the values of both channels<br />
When only <strong>one</strong> channel is measured, the controls of the other channel are disabled or removed from the display.<br />
The Spectrum Analyzer<br />
61