Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>11</strong>4 CHAPTER 7 Wide Area Networking<br />
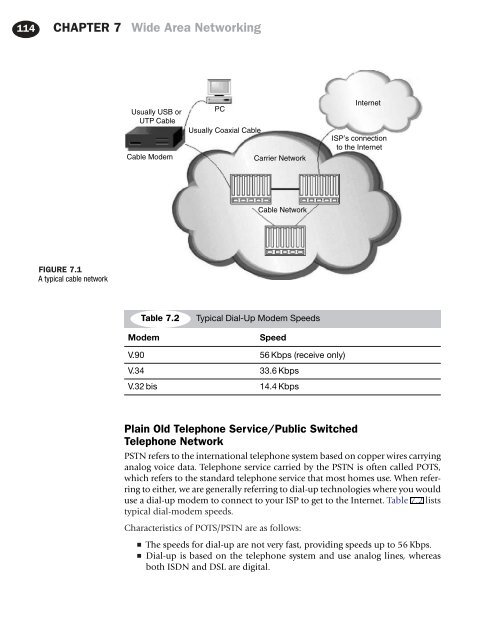
Usually USB or<br />
UTP Cable<br />
Cable Modem<br />
PC<br />
Usually Coaxial Cable<br />
Carrier Network<br />
Internet<br />
ISP’s connection<br />
to the Internet<br />
Cable Network<br />
FIGURE 7.1<br />
A typical cable network<br />
Table 7.2<br />
Modem<br />
Typical Dial-Up Modem Speeds<br />
Speed<br />
V.90 56 Kbps (receive only)<br />
V.34 33.6 Kbps<br />
V.32 bis 14.4 Kbps<br />
Plain Old Telephone Service/Public Switched<br />
Telephone Network<br />
PSTN refers to the international telephone system based on copper wires carrying<br />
analog voice data. Telephone service carried by the PSTN is often called POTS,<br />
which refers to the standard telephone service that most homes use. When referring<br />
to either, we are generally referring to dial-up technologies where you would<br />
use a dial-up modem to connect to your ISP to get to the Internet. Table 7.2 lists<br />
typical dial-modem speeds.<br />
Characteristics of POTS/PSTN are as follows:<br />
■ The speeds for dial-up are not very fast, providing speeds up to 56 Kbps.<br />
■ Dial-up is based on the telephone system and use analog lines, whereas<br />
both ISDN and DSL are digital.