Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
92 CHAPTER 6 TCP/IP and Routing<br />
For example, the binary value of 00101001 would be translated to: 32 + 8 +<br />
1 = 41.<br />
Network ID and Host ID<br />
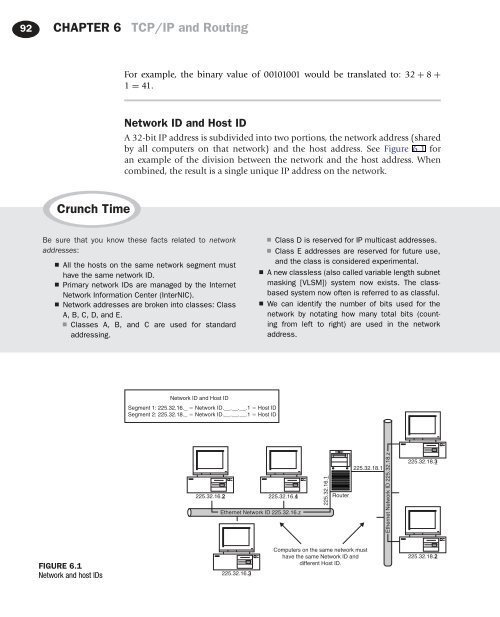
A 32-bit IP address is subdivided into two portions, the network address (shared<br />
by all computers on that network) and the host address. See Figure 6.1 for<br />
an example of the division between the network and the host address. When<br />
combined, the result is a single unique IP address on the network.<br />
Crunch Time<br />
Be sure that you know these facts related to network<br />
addresses:<br />
■ All the hosts on the same network segment must<br />
have the same network ID.<br />
■ Primary network IDs are managed by the Internet<br />
Network Information Center (InterNIC).<br />
■ Network addresses are broken into classes: Class<br />
A, B, C, D, and E.<br />
■ Classes A, B, and C are used for standard<br />
addressing.<br />
■ Class D is reserved for IP multicast addresses.<br />
■ Class E addresses are reserved for future use,<br />
and the class is considered experimental.<br />
■ A new classless (also called variable length subnet<br />
masking [VLSM]) system now exists. The classbased<br />
system now often is referred to as classful.<br />
■ We can identify the number of bits used for the<br />
network by notating how many total bits (counting<br />
from left to right) are used in the network<br />
address.<br />
Network ID and Host ID<br />
Segment 1: 225.32.16._ 5 Network ID.__.__.__.1 5 Host ID<br />
Segment 2: 225.32.18._ 5 Network ID.__.__.__.1 5 Host ID<br />
225.32.16.2_<br />
225.32.16.4_<br />
Ethernet Network ID 225.32.16.z<br />
225.32.16.1_<br />
Router<br />
225.32.18.1<br />
Ethernet Network ID 225.32.18.z<br />
225.32.18.3_<br />
FIGURE 6.1<br />
Network and host IDs<br />
225.32.16.3_<br />
Computers on the same network must<br />
have the same Network ID and<br />
different Host ID.<br />
225.32.18.2_