Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Media Issues 23<br />
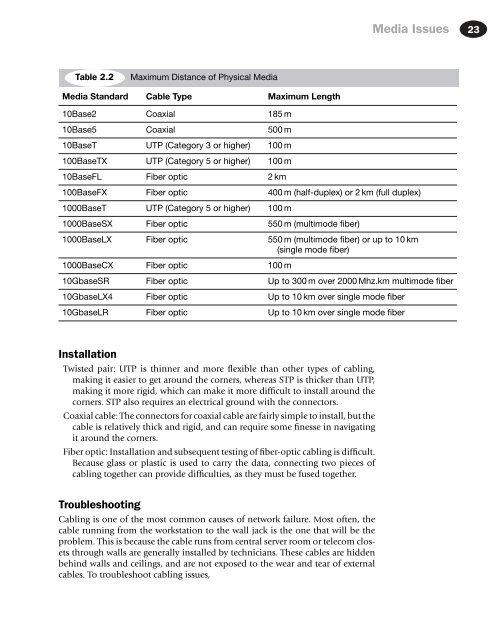
Table 2.2<br />
Maximum Distance of Physical Media<br />
Media Standard Cable Type Maximum Length<br />
10Base2 Coaxial 185 m<br />
10Base5 Coaxial 500 m<br />
10BaseT UTP (Category 3 or higher) 100 m<br />
100BaseTX UTP (Category 5 or higher) 100 m<br />
10BaseFL Fiber optic 2 km<br />
100BaseFX Fiber optic 400 m (half-duplex) or 2 km (full duplex)<br />
1000BaseT UTP (Category 5 or higher) 100 m<br />
1000BaseSX Fiber optic 550 m (multimode fiber)<br />
1000BaseLX Fiber optic 550 m (multimode fiber) or up to 10 km<br />
(single mode fiber)<br />
1000BaseCX Fiber optic 100 m<br />
10GbaseSR Fiber optic Up to 300 m over 2000 Mhz.km multimode fiber<br />
10GbaseLX4 Fiber optic Up to 10 km over single mode fiber<br />
10GbaseLR Fiber optic Up to 10 km over single mode fiber<br />
Installation<br />
Twisted pair: UTP is thinner and more flexible than other types of cabling,<br />
making it easier to get around the corners, whereas STP is thicker than UTP,<br />
making it more rigid, which can make it more difficult to install around the<br />
corners. STP also requires an electrical ground with the connectors.<br />
Coaxial cable: The connectors for coaxial cable are fairly simple to install, but the<br />
cable is relatively thick and rigid, and can require some finesse in navigating<br />
it around the corners.<br />
Fiber optic: Installation and subsequent testing of fiber-optic cabling is difficult.<br />
Because glass or plastic is used to carry the data, connecting two pieces of<br />
cabling together can provide difficulties, as they must be fused together.<br />
Troubleshooting<br />
Cabling is one of the most common causes of network failure. Most often, the<br />
cable running from the workstation to the wall jack is the one that will be the<br />
problem. This is because the cable runs from central server room or telecom closets<br />
through walls are generally installed by technicians. These cables are hidden<br />
behind walls and ceilings, and are not exposed to the wear and tear of external<br />
cables. To troubleshoot cabling issues,