Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
48 CHAPTER 3 Network Devices<br />
■ Dual-homed host firewalls A dual-homed firewall consists of a single computer with<br />
two physical network interfaces. This computer acts as a gateway between two<br />
networks.<br />
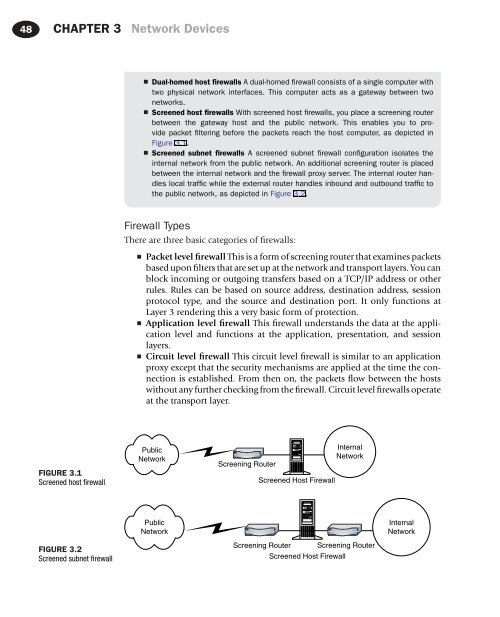
■ Screened host firewalls With screened host firewalls, you place a screening router<br />
between the gateway host and the public network. This enables you to provide<br />
packet filtering before the packets reach the host computer, as depicted in<br />
Figure 3.1.<br />
■ Screened subnet firewalls A screened subnet firewall configuration isolates the<br />
internal network from the public network. An additional screening router is placed<br />
between the internal network and the firewall proxy server. The internal router handles<br />
local traffic while the external router handles inbound and outbound traffic to<br />
the public network, as depicted in Figure 3.2.<br />
Firewall Types<br />
There are three basic categories of firewalls:<br />
■<br />
■<br />
■<br />
Packet level firewall This is a form of screening router that examines packets<br />
based upon filters that are set up at the network and transport layers. You can<br />
block incoming or outgoing transfers based on a TCP/IP address or other<br />
rules. Rules can be based on source address, destination address, session<br />
protocol type, and the source and destination port. It only functions at<br />
Layer 3 rendering this a very basic form of protection.<br />
Application level firewall This firewall understands the data at the application<br />
level and functions at the application, presentation, and session<br />
layers.<br />
Circuit level firewall This circuit level firewall is similar to an application<br />
proxy except that the security mechanisms are applied at the time the connection<br />
is established. From then on, the packets flow between the hosts<br />
without any further checking from the firewall. Circuit level firewalls operate<br />
at the transport layer.<br />
FIGURE 3.1<br />
Screened host firewall<br />
Public<br />
Network<br />
Screening Router<br />
Screened Host Firewall<br />
Internal<br />
Network<br />
FIGURE 3.2<br />
Screened subnet firewall<br />
Public<br />
Network<br />
Screening Router Screening Router<br />
Screened Host Firewall<br />
Internal<br />
Network