Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
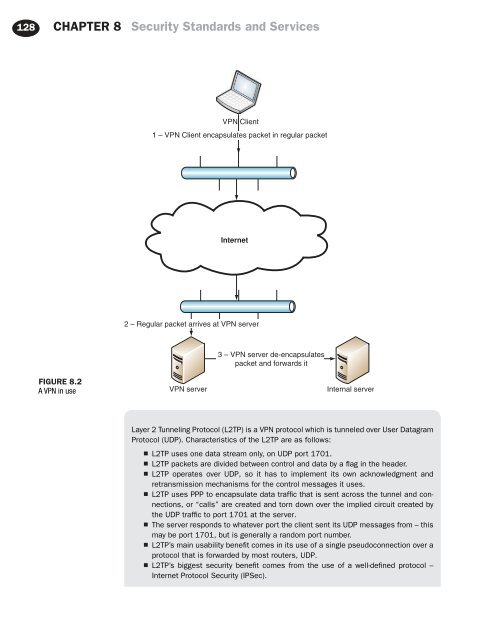
128 CHAPTER 8 Security Standards and Services<br />
VPN Client<br />
1 – VPN Client encapsulates packet in regular packet<br />
Internet<br />
2 – Regular packet arrives at VPN server<br />
3 – VPN server de-encapsulates<br />
packet and forwards it<br />
FIGURE 8.2<br />
A VPN in use<br />
VPN server<br />
Internal server<br />
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a VPN protocol which is tunneled over User Datagram<br />
Protocol (UDP). Characteristics of the L2TP are as follows:<br />
■ L2TP uses one data stream only, on UDP port 1701.<br />
■ L2TP packets are divided between control and data by a flag in the header.<br />
■ L2TP operates over UDP, so it has to implement its own acknowledgment and<br />
retransmission mechanisms for the control messages it uses.<br />
■ L2TP uses PPP to encapsulate data traffic that is sent across the tunnel and connections,<br />
or “calls” are created and torn down over the implied circuit created by<br />
the UDP traffic to port 1701 at the server.<br />
■ The server responds to whatever port the client sent its UDP messages from – this<br />
may be port 1701, but is generally a random port number.<br />
■ L2TP’s main usability benefit comes in its use of a single pseudoconnection over a<br />
protocol that is forwarded by most routers, UDP.<br />
■ L2TP’s biggest security benefit comes from the use of a well-defined protocol –<br />
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec).