Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
Syngress - Eleventh Hour Network+ Exam N10-004 Study Guide (11 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Network Monitoring 149<br />
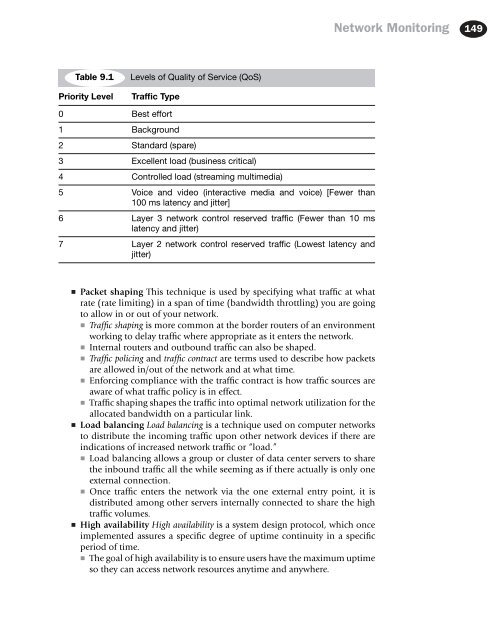
Table 9.1<br />
Priority Level<br />
Levels of Quality of Service (QoS)<br />
Traffic Type<br />
0 Best effort<br />
1 Background<br />
2 Standard (spare)<br />
3 Excellent load (business critical)<br />
4 Controlled load (streaming multimedia)<br />
5 Voice and video (interactive media and voice) [Fewer than<br />
100 ms latency and jitter]<br />
6 Layer 3 network control reserved traffic (Fewer than 10 ms<br />
latency and jitter)<br />
7 Layer 2 network control reserved traffic (Lowest latency and<br />
jitter)<br />
■ Packet shaping This technique is used by specifying what traffic at what<br />
rate (rate limiting) in a span of time (bandwidth throttling) you are going<br />
to allow in or out of your network.<br />
■ Traffic shaping is more common at the border routers of an environment<br />
working to delay traffic where appropriate as it enters the network.<br />
■ Internal routers and outbound traffic can also be shaped.<br />
■ Traffic policing and traffic contract are terms used to describe how packets<br />
are allowed in/out of the network and at what time.<br />
■ Enforcing compliance with the traffic contract is how traffic sources are<br />
aware of what traffic policy is in effect.<br />
■ Traffic shaping shapes the traffic into optimal network utilization for the<br />
allocated bandwidth on a particular link.<br />
■ Load balancing Load balancing is a technique used on computer networks<br />
to distribute the incoming traffic upon other network devices if there are<br />
indications of increased network traffic or “load.”<br />
■ Load balancing allows a group or cluster of data center servers to share<br />
the inbound traffic all the while seeming as if there actually is only one<br />
external connection.<br />
■ Once traffic enters the network via the one external entry point, it is<br />
distributed among other servers internally connected to share the high<br />
traffic volumes.<br />
■ High availability High availability is a system design protocol, which once<br />
implemented assures a specific degree of uptime continuity in a specific<br />
period of time.<br />
■ The goal of high availability is to ensure users have the maximum uptime<br />
so they can access network resources anytime and anywhere.