iaea human health series publications - SEDIM
iaea human health series publications - SEDIM
iaea human health series publications - SEDIM
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
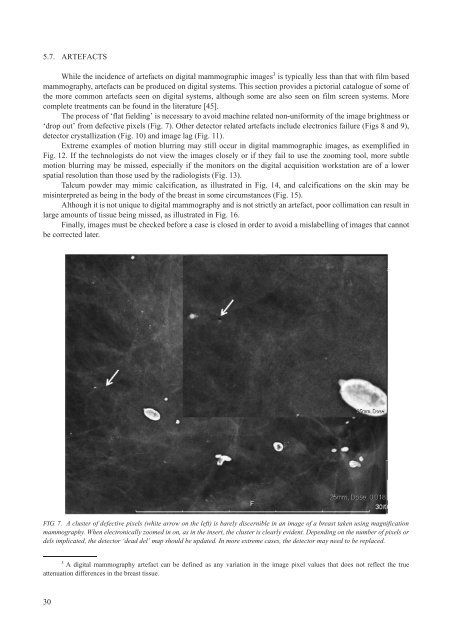
5.7. ARTEFACTSWhile the incidence of artefacts on digital mammographic images 3 is typically less than that with film basedmammography, artefacts can be produced on digital systems. This section provides a pictorial catalogue of some ofthe more common artefacts seen on digital systems, although some are also seen on film screen systems. Morecomplete treatments can be found in the literature [45].The process of ‘flat fielding’ is necessary to avoid machine related non-uniformity of the image brightness or‘drop out’ from defective pixels (Fig. 7). Other detector related artefacts include electronics failure (Figs 8 and 9),detector crystallization (Fig. 10) and image lag (Fig. 11).Extreme examples of motion blurring may still occur in digital mammographic images, as exemplified inFig. 12. If the technologists do not view the images closely or if they fail to use the zooming tool, more subtlemotion blurring may be missed, especially if the monitors on the digital acquisition workstation are of a lowerspatial resolution than those used by the radiologists (Fig. 13).Talcum powder may mimic calcification, as illustrated in Fig. 14, and calcifications on the skin may bemisinterpreted as being in the body of the breast in some circumstances (Fig. 15).Although it is not unique to digital mammography and is not strictly an artefact, poor collimation can result inlarge amounts of tissue being missed, as illustrated in Fig. 16.Finally, images must be checked before a case is closed in order to avoid a mislabelling of images that cannotbe corrected later.FIG. 7. A cluster of defective pixels (white arrow on the left) is barely discernible in an image of a breast taken using magnificationmammography. When electronically zoomed in on, as in the insert, the cluster is clearly evident. Depending on the number of pixels ordels implicated, the detector ‘dead del’ map should be updated. In more extreme cases, the detector may need to be replaced.3A digital mammography artefact can be defined as any variation in the image pixel values that does not reflect the trueattenuation differences in the breast tissue.30