The mechanical effects of short-circuit currents in - Montefiore
The mechanical effects of short-circuit currents in - Montefiore
The mechanical effects of short-circuit currents in - Montefiore
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
small sub-conductor separation as/ds, the p<strong>in</strong>ch is<br />
generally very limited and its duration is also<br />
very <strong>short</strong>. <strong>The</strong> oscillograms <strong>in</strong> Figure 3.5 to<br />
Figure 3.8 show clearly the electromagnetic<br />
force (the 50 Hz can be seen, progressively<br />
transferred to 100 Hz) with a sudden peak, just at<br />
the <strong>in</strong>stance <strong>of</strong> contact. In the case <strong>of</strong> very large<br />
subspan and very <strong>short</strong> sub-conductor separation,<br />
the p<strong>in</strong>ch is noticeable smaller, Figure 3.5. It is<br />
quite obvious that the situation is similar to<br />
Figure 3.3, s<strong>in</strong>gle stra<strong>in</strong> conductor.<br />
Figure 3.5 Tensile force with bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong><br />
conductor; similar to case *8, tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
very large subspan length, <strong>short</strong> sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 400; as/ds = 1,9, λ = 211<br />
Figure 3.6 Tensile force with bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a slack<br />
conductor; case 3, Figure 1a; tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
large subspan length, <strong>short</strong> sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 79; as/ds = 1,9; λ = 40<br />
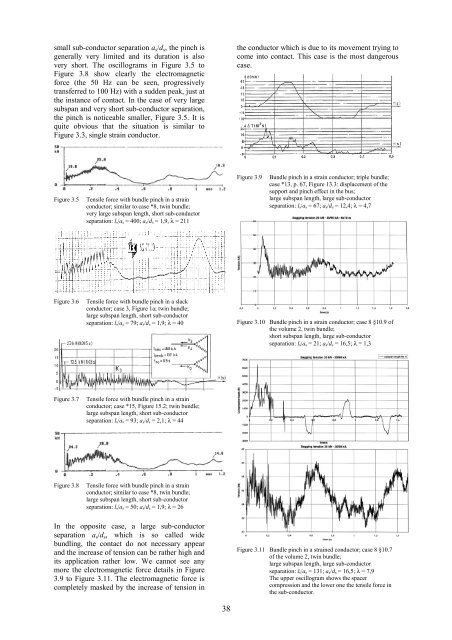
Figure 3.7 Tensile force with bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong><br />
conductor; case *15, Figure 15.2; tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
large subspan length, <strong>short</strong> sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 93; as/ds = 2,1; λ = 44<br />
Figure 3.8 Tensile force with bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong><br />
conductor; similar to case *8, tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
large subspan length, <strong>short</strong> sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 50; as/ds = 1,9; λ = 26<br />
In the opposite case, a large sub-conductor<br />
separation as/ds, which is so called wide<br />
bundl<strong>in</strong>g, the contact do not necessary appear<br />
and the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>of</strong> tension can be rather high and<br />
its application rather low. We cannot see any<br />
more the electromagnetic force details <strong>in</strong> Figure<br />
3.9 to Figure 3.11. <strong>The</strong> electromagnetic force is<br />
completely masked by the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>of</strong> tension <strong>in</strong><br />
38<br />
the conductor which is due to its movement try<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
come <strong>in</strong>to contact. This case is the most dangerous<br />
case.<br />
Figure 3.9 Bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong> conductor; triple bundle;<br />
case *13, p. 67, Figure 13.3: displacement <strong>of</strong> the<br />
support and p<strong>in</strong>ch effect <strong>in</strong> the bus;<br />
large subspan length, large sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 67; as/ds = 12,4; λ = 4,7<br />
Figure 3.10 Bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong> conductor; case 8 §10.9 <strong>of</strong><br />
the volume 2, tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
<strong>short</strong> subspan length, large sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 21; as/ds = 16,5; λ = 1,3<br />
Figure 3.11 Bundle p<strong>in</strong>ch <strong>in</strong> a stra<strong>in</strong>ed conductor; case 8 §10.7<br />
<strong>of</strong> the volume 2, tw<strong>in</strong> bundle;<br />
large subspan length, large sub-conductor<br />
separation: ls/as = 131; as/ds = 16,5; λ = 7,9<br />
<strong>The</strong> upper oscillogram shows the spacer<br />
compression and the lower one the tensile force <strong>in</strong><br />
the sub-conductor.