Applied numerical modeling of saturated / unsaturated flow and ...
Applied numerical modeling of saturated / unsaturated flow and ...
Applied numerical modeling of saturated / unsaturated flow and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
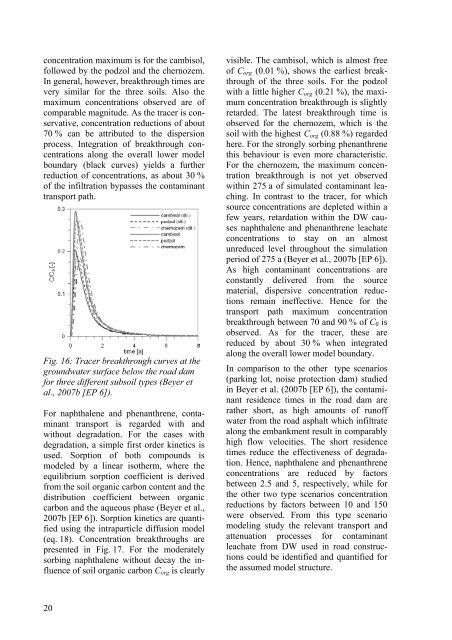
concentration maximum is for the cambisol,<br />
followed by the podzol <strong>and</strong> the chernozem.<br />
In general, however, breakthrough times are<br />
very similar for the three soils. Also the<br />
maximum concentrations observed are <strong>of</strong><br />
comparable magnitude. As the tracer is conservative,<br />
concentration reductions <strong>of</strong> about<br />
70 % can be attributed to the dispersion<br />
process. Integration <strong>of</strong> breakthrough concentrations<br />
along the overall lower model<br />
boundary (black curves) yields a further<br />
reduction <strong>of</strong> concentrations, as about 30 %<br />
<strong>of</strong> the infiltration bypasses the contaminant<br />
transport path.<br />
Fig. 16: Tracer breakthrough curves at the<br />
groundwater surface below the road dam<br />
for three different subsoil types (Beyer et<br />
al., 2007b [EP 6]).<br />
For naphthalene <strong>and</strong> phenanthrene, contaminant<br />
transport is regarded with <strong>and</strong><br />
without degradation. For the cases with<br />
degradation, a simple first order kinetics is<br />
used. Sorption <strong>of</strong> both compounds is<br />
modeled by a linear isotherm, where the<br />
equilibrium sorption coefficient is derived<br />
from the soil organic carbon content <strong>and</strong> the<br />
distribution coefficient between organic<br />
carbon <strong>and</strong> the aqueous phase (Beyer et al.,<br />
2007b [EP 6]). Sorption kinetics are quantified<br />
using the intraparticle diffusion model<br />
(eq. 18). Concentration breakthroughs are<br />
presented in Fig. 17. For the moderately<br />
sorbing naphthalene without decay the influence<br />
<strong>of</strong> soil organic carbon Corg is clearly<br />
20<br />
visible. The cambisol, which is almost free<br />
<strong>of</strong> Corg (0.01 %), shows the earliest breakthrough<br />
<strong>of</strong> the three soils. For the podzol<br />
with a little higher Corg (0.21 %), the maximum<br />
concentration breakthrough is slightly<br />
retarded. The latest breakthrough time is<br />
observed for the chernozem, which is the<br />
soil with the highest Corg (0.88 %) regarded<br />
here. For the strongly sorbing phenanthrene<br />
this behaviour is even more characteristic.<br />
For the chernozem, the maximum concentration<br />
breakthrough is not yet observed<br />
within 275 a <strong>of</strong> simulated contaminant leaching.<br />
In contrast to the tracer, for which<br />
source concentrations are depleted within a<br />
few years, retardation within the DW causes<br />
naphthalene <strong>and</strong> phenanthrene leachate<br />
concentrations to stay on an almost<br />
unreduced level throughout the simulation<br />
period <strong>of</strong> 275 a (Beyer et al., 2007b [EP 6]).<br />
As high contaminant concentrations are<br />
constantly delivered from the source<br />
material, dispersive concentration reductions<br />
remain ineffective. Hence for the<br />
transport path maximum concentration<br />
breakthrough between 70 <strong>and</strong> 90 % <strong>of</strong> C0 is<br />
observed. As for the tracer, these are<br />
reduced by about 30 % when integrated<br />
along the overall lower model boundary.<br />
In comparison to the other type scenarios<br />
(parking lot, noise protection dam) studied<br />
in Beyer et al. (2007b [EP 6]), the contaminant<br />
residence times in the road dam are<br />
rather short, as high amounts <strong>of</strong> run<strong>of</strong>f<br />
water from the road asphalt which infiltrate<br />
along the embankment result in comparably<br />
high <strong>flow</strong> velocities. The short residence<br />
times reduce the effectiveness <strong>of</strong> degradation.<br />
Hence, naphthalene <strong>and</strong> phenanthrene<br />
concentrations are reduced by factors<br />
between 2.5 <strong>and</strong> 5, respectively, while for<br />
the other two type scenarios concentration<br />
reductions by factors between 10 <strong>and</strong> 150<br />
were observed. From this type scenario<br />
<strong>modeling</strong> study the relevant transport <strong>and</strong><br />
attenuation processes for contaminant<br />
leachate from DW used in road constructions<br />
could be identified <strong>and</strong> quantified for<br />
the assumed model structure.