Memoria (spa) (5.02MB)
Memoria (spa) (5.02MB)
Memoria (spa) (5.02MB)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ANÁLISIS DE UN KART DE COMPETICIÓN Y DE<br />
SUS COMPONENTES<br />
Rr = µr · Pom<br />
Ra = ·.<br />
<br />
· <br />
Rp = 0, ya que calculamos la aceleración en llano.<br />
80,00<br />
60,00<br />
40,00<br />
20,00<br />
0,00<br />
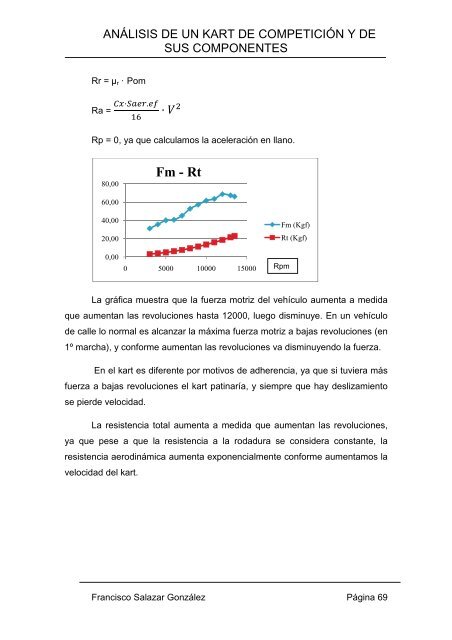
La gráfica muestra que la fuerza motriz del vehículo aumenta a medida<br />
que aumentan las revoluciones hasta 12000, luego disminuye. En un vehículo<br />
de calle lo normal es alcanzar la máxima fuerza motriz a bajas revoluciones (en<br />
1º marcha), y conforme aumentan las revoluciones va disminuyendo la fuerza.<br />
En el kart es diferente por motivos de adherencia, ya que si tuviera más<br />
fuerza a bajas revoluciones el kart patinaría, y siempre que hay deslizamiento<br />
se pierde velocidad.<br />
La resistencia total aumenta a medida que aumentan las revoluciones,<br />
ya que pese a que la resistencia a la rodadura se considera constante, la<br />
resistencia aerodinámica aumenta exponencialmente conforme aumentamos la<br />
velocidad del kart.<br />
Fm - Rt<br />
0 5000 10000 15000<br />
Fm (Kgf)<br />
Rt (Kgf)<br />
Rpm<br />
Francisco Salazar González Página 69