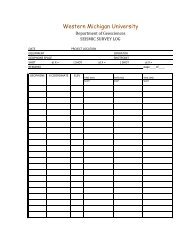
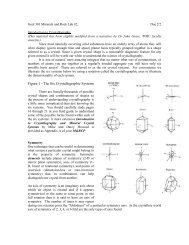
Using ArcCatalog
Using ArcCatalog
Using ArcCatalog
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
subtype<br />
In a geodatabase, subtypes are used to break the features in a<br />
feature class into major categories. For example, the streets in a<br />
streets feature class could be categorized into three subtypes:<br />
local streets, collector streets, and arterial streets. Subtypes<br />
differentiate objects based on their rules. Default properties can<br />
be assigned to subtypes so that new features inherit the<br />
properties of their subtype. For example, a local street subtype<br />
might be defined so that whenever this type of street is added to<br />
the feature class its speed limit attribute is automatically set to<br />
fifty miles per hour.<br />
surface<br />
A geographic phenomenon represented as a set of continuous<br />
data, such as elevation or air temperature over an area, or the<br />
boundary between two distinct materials or processes. A clear or<br />
sharp break in values of the phenomenon (breaklines) indicates a<br />
significant change in the structure of the phenomenon, such as a<br />
cliff, not a change in geographic feature. Surfaces can be<br />
represented by models built from regularly or irregularly spaced<br />
sample points on the surface, or by contour lines, isolines,<br />
bathymetry, or the like.<br />
symbol<br />
A graphic representation of a geographic feature or feature class<br />
on a map. For example, line symbols represent arc features; marker<br />
symbols, points; shade symbols, polygons; and text symbols,<br />
annotation. Many characteristics define symbols including color,<br />
size, angle, and pattern.<br />
symbology<br />
The criteria used to determine symbols for the features in a layer.<br />
A characteristic of a feature may influence the size, color, and<br />
shape of the symbol used.<br />
table<br />
1. A set of data elements arranged in rows and columns. Each row<br />
represents an individual entity, record, or feature and each<br />
column represents a single field or attribute value. A table has a<br />
specified number of columns but can have any number of rows.<br />
2. In ArcView GIS 3, one of the five types of documents that can<br />
be contained within a project file. A table stores attribute data.<br />
table of contents<br />
A list of data frames and layers on a map that show how the data<br />
is symbolized.<br />
tabular data<br />
Descriptive information, usually alphanumeric, that is stored in<br />
rows and columns in a database and can be linked to map<br />
features. See also table.<br />
TCP/IP<br />
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). A communication protocol<br />
layered above the Internet Protocol (IP). These are a suite of<br />
nonproprietary communication protocols, or sets of rules, that<br />
allow computers to send and receive data over networks.<br />
template<br />
See map template.<br />
text box<br />
An entity that displays text entered by a user or derived from<br />
another source for editing purposes.<br />
thumbnail<br />
A snapshot describing the geographic data contained in a data<br />
source or layer, or a map layout. A thumbnail might provide an<br />
overview of all the features in a feature class or a detailed view of<br />
the features in, and the symbology of, a layer. Thumbnails are not<br />
GLOSSARY 277