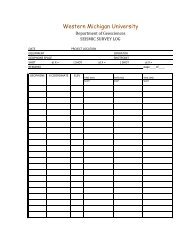
Using ArcCatalog
Using ArcCatalog
Using ArcCatalog
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Geodatabases<br />
Geodatabases are relational databases that contain geographic<br />
information. Geodatabases contain feature classes and tables.<br />
Feature classes can be organized into a feature dataset; they can<br />
also exist independently in the geodatabase.<br />
Feature classes store geographic features represented as points,<br />
lines, polygons, annotation, dimensions, and multipatches and<br />
their attributes. All feature classes in a feature dataset share the<br />
same coordinate system. Tables may contain additional attributes<br />
for a feature class or geographic information such as addresses or<br />
x,y,z coordinates.<br />
Many objects in a geodatabase can be related to each other. For<br />
example, tables containing customer addresses and billing<br />
information are related, just as state and county feature classes<br />
are related. To explicitly define the relationships between objects<br />
in a geodatabase, you must create a relationship class. Relationships<br />
let you use attributes stored in a related object to symbolize,<br />
label, or query a feature class.<br />
Feature classes in a feature dataset can be organized into a<br />
geometric network or a topology. A geometric network combines<br />
line and point feature classes to model linear networks—for<br />
example, electrical networks—and maintains topological relationships<br />
between its feature classes. A topology is a set of relationships<br />
that define how the features in one or more feature classes<br />
share geometry—for example, cities must be properly inside<br />
states.<br />
Creating and accessing geodatabases<br />
To manage your own spatial database, you can create a personal<br />
geodatabase. If you do this, your data will be stored in a<br />
Microsoft Access database. For a multiuser spatial database, use<br />
ArcSDE, which lets many people in an organization simultaneously<br />
update data stored in a centrally located RDBMS. SDE ®<br />
for Coverages lets you access coverage, ArcStorm, or ArcInfo<br />
Librarian databases just as you would an RDBMS.<br />
You can access personal geodatabases directly in <strong>ArcCatalog</strong>,<br />
but to access data stored in an RDBMS you must add a database<br />
connection. To do so, double-click one of the Add Database<br />
Connection wizards in the Database Connections folder. You’ll be<br />
prompted for information such as your username and password<br />
and the database to which you want to connect.<br />
In general, when you create a database connection, you choose<br />
the data provider that will retrieve your data from the database.<br />
For multiuser spatial databases, ArcSDE is the data provider.<br />
Object Linking and Embedding Database (OLE DB) providers<br />
generally retrieve nonspatial data only. You can preview these<br />
tables in <strong>ArcCatalog</strong> and join their values to spatial data. If an<br />
OLE DB provider can retrieve spatial data and present it in Open<br />
GIS Consortium, Inc. (OpenGIS ® or OGC), format, you can<br />
preview that data in the Catalog.<br />
All database connections are stored in the Database Connections<br />
folder by default, but they can be moved elsewhere. For example,<br />
you can place a connection that has read-only access to the<br />
database in a shared folder where others can access it; they can<br />
use it to view the database’s contents in the Catalog without<br />
having to know the details of how to connect to the database.<br />
The first time you select a database connection, <strong>ArcCatalog</strong> tries<br />
to connect to the database. If the connection attempt is successful,<br />
<strong>ArcCatalog</strong> will list the items contained in the database. When<br />
you see a little red x on the database connection’s icon, it is<br />
disconnected; until you have reestablished the connection, you<br />
can’t access data stored in the database.<br />
Items in an RDBMS are owned by the user who created them.<br />
When <strong>ArcCatalog</strong> lists the contents of an ArcSDE geodatabase,<br />
the owner’s name appears before the item’s name. For example, a<br />
feature class named valves that is owned by the user admin<br />
would appear in the Catalog as admin.valves. If the RDBMS<br />
supports databases, such as SQL Server, the database name<br />
will appear between the owner’s name and the object’s name.<br />
56 USING ARCCATALOG