You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
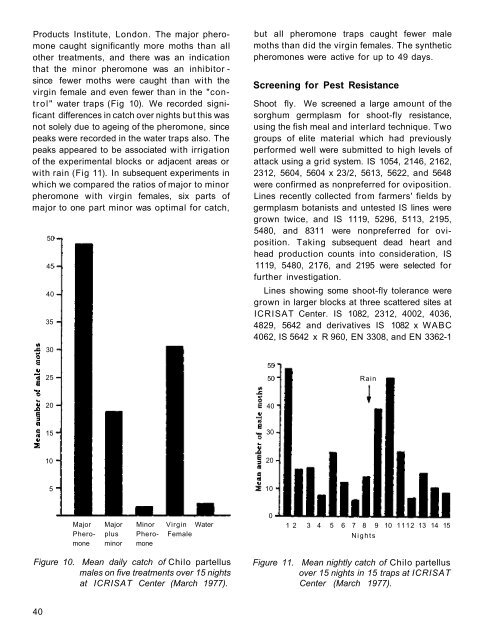
Products Institute, London. The major pheromone<br />
caught significantly more moths than all<br />
other treatments, and there was an indication<br />
that the minor pheromone was an inhibitor -<br />
since fewer moths were caught than with the<br />
virgin female and even fewer than in the "control"<br />
water traps (Fig 10). We recorded significant<br />
differences in catch over nights but this was<br />
not solely due to ageing of the pheromone, since<br />
peaks were recorded in the water traps also. The<br />
peaks appeared to be associated with irrigation<br />
of the experimental blocks or adjacent areas or<br />
with rain (Fig 11). In subsequent experiments in<br />
which we compared the ratios of major to minor<br />
pheromone with virgin females, six parts of<br />
major to one part minor was optimal for catch,<br />
50<br />
45<br />
40<br />
35<br />
30<br />
but all pheromone traps caught fewer male<br />
moths than did the virgin females. The synthetic<br />
pheromones were active for up to 49 days.<br />
Screening for Pest Resistance<br />
Shoot fly. We screened a large amount of the<br />
sorghum germplasm for shoot-fly resistance,<br />
using the fish meal and interlard technique. Two<br />
groups of elite material which had previously<br />
performed well were submitted to high levels of<br />
attack using a grid system. IS 1054, 2146, 2162,<br />
2312, 5604, 5604 x 23/2, 5613, 5622, and 5648<br />
were confirmed as nonpreferred for oviposition.<br />
Lines recently collected from farmers' fields by<br />
germplasm botanists and untested IS lines were<br />
grown twice, and IS 1119, 5296, 5113, 2195,<br />
5480, and 8311 were nonpreferred for oviposition.<br />
Taking subsequent dead heart and<br />
head production counts into consideration, IS<br />
1119, 5480, 2176, and 2195 were selected for<br />
further investigation.<br />
Lines showing some shoot-fly tolerance were<br />
grown in larger blocks at three scattered sites at<br />
ICRISAT Center. IS 1082, 2312, 4002, 4036,<br />
4829, 5642 and derivatives IS 1082 x WABC<br />
4062, IS 5642 x R 960, EN 3308, and EN 3362-1<br />
25<br />
55<br />
50<br />
Rain<br />
20<br />
40<br />
15<br />
30<br />
10<br />
20<br />
5<br />
10<br />
Major Major Minor Virgin Water<br />
Phero- plus Phero- Female<br />
mone minor mone<br />
0<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1112 13 14 15<br />
N i g h t s<br />
Figure 10. Mean daily catch of Chilo partellus<br />
males on five treatments over 15 nights<br />
at ICRISAT Center (March 1977).<br />
Figure 11. Mean nightly catch of Chilo partellus<br />
over 15 nights in 15 traps at ICRISAT<br />
Center (March 1977).<br />
40