Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
244<br />
Time invariant input parameter processing for applications in the<br />
COSMO-CLM Model<br />
Gerhard Smiatek 1 , Goran Georgievski 2 and Hermann Asensio 3<br />
1 Institute for Meteorology and Climate Research, Atmospheric Environmental Research (IMK-IFU), Forschungszentrum<br />
Karlsruhe GmbH (gerhard.smiatek@imk.fzk.de<br />
2 BTU Cottbus, Chair of Environmental Meteorology (goran.georgievski@tu-cottbus.de)<br />
3 Deutscher Wetterdienst, (hermann.asensio@dwd.de)<br />
1. Introduction<br />
Topography, soil characteristics, land use and land cover<br />
as well as associated vegetation parameters are key<br />
information in Soil-vegetation-Atmosphere-Transfer<br />
(SVAT) schemes widely applied in atmospheric models<br />
in parameterization of surface exchange processes. With<br />
exception of seasonal changes in the leaf area index<br />
(LAI), vegetation fraction or roughness length, the<br />
geodata input is usually kept constant in a simulation and<br />
can therefore be considered as a time-invariant<br />
parameter..<br />
2. Data Processing<br />
The quality of the data input can have a significant<br />
influence on the simulation results. Block (2007) has<br />
shown changes of annual mean values in the order of<br />
0.25 K for the 2m-temperature related to the source of the<br />
leaf area index data, vegetation cover, soil data, and<br />
derived parameters. Box and Rinke (2003) identified<br />
systematic model biases of GTOPO30 elevation data set<br />
over Greenland. In 50 km grid cells employed by the<br />
HIRHAM regional climate model the errors ranged up to<br />
−840 meters.<br />
Errors result not only from the quality of the globally<br />
available data sets on topography, soil characteristics and<br />
land use but also from way how these data are processed.<br />
Investigations with various compilers and compiler<br />
options revealed differences up to 20 meters in the<br />
average elevation in some model grid cells covering<br />
complex terrain. Slightly reduced precision in the domain<br />
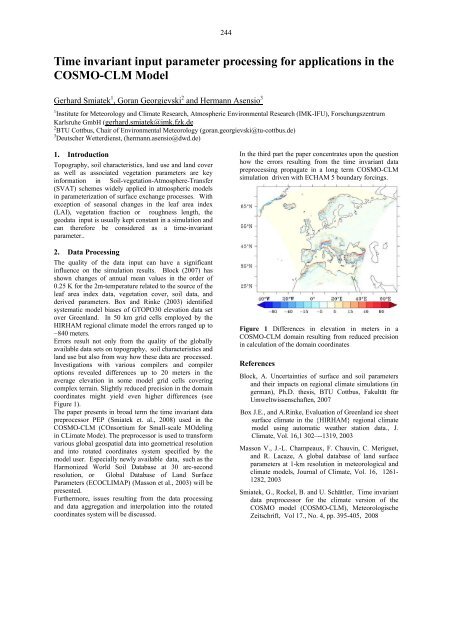
coordinates might yield even higher differences (see<br />
Figure 1).<br />
The paper presents in broad term the time invariant data<br />
preprocessor PEP (Smiatek et. al., 2008) used in the<br />
COSMO-CLM (COnsortium for Small-scale MOdeling<br />
in CLimate Mode). The preprocessor is used to transform<br />
various global geospatial data into geometrical resolution<br />
and into rotated coordinates system specified by the<br />
model user. Especially newly available data, such as the<br />
Harmonized World Soil Database at 30 arc-second<br />
resolution, or Global Database of Land Surface<br />
Parameters (ECOCLIMAP) (Masson et al., 2003) will be<br />
presented.<br />
Furthermore, issues resulting from the data processing<br />
and data aggregation and interpolation into the rotated<br />
coordinates system will be discussed.<br />
In the third part the paper concentrates upon the question<br />
how the errors resulting from the time invariant data<br />
preprocessing propagate in a long term COSMO-CLM<br />
simulation driven with ECHAM 5 boundary forcings.<br />
Figure 1 Differences in elevation in meters in a<br />
COSMO-CLM domain resulting from reduced precision<br />
in calculation of the domain coordinates<br />
References<br />
Block, A. Uncertainties of surface and soil parameters<br />
and their impacts on regional climate simulations (in<br />
german), Ph.D. thesis, BTU Cottbus, Fakultät für<br />
Umweltwissenschaften, 2007<br />
Box J.E., and A.Rinke, Evaluation of Greenland ice sheet<br />
surface climate in the {HIRHAM} regional climate<br />
model using automatic weather station data., J.<br />
Climate, Vol. 16,1 302–--1319, 2003<br />
Masson V., J.-L. Champeaux, F. Chauvin, C. Meriguet,<br />
and R. Lacaze, A global database of land surface<br />
parameters at 1-km resolution in meteorological and<br />
climate models, Journal of Climate, Vol. 16, 1261-<br />
1282, 2003<br />
Smiatek, G., Rockel, B. and U. Schättler, Time invariant<br />
data preprocessor for the climate version of the<br />
COSMO model (COSMO-CLM), Meteorologische<br />
Zeitschrift, Vol 17., No. 4, pp. 395-405, 2008