Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
Low (web) Quality - BALTEX
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
289<br />
In April 2000, the fire emissions are relatively low, but<br />
produce an impact area of comparable size to the impact<br />
area of megacitiy emissions, which is mostly located<br />
away form coastal regions.<br />
During the fire-season, the fire impact area is much<br />
larger, while the impact of the megacity emissions on air<br />
quality is of the same magnitude (not shown).<br />
Further research will lead to a deeper understanding and<br />
quantification of the impact of the different emission<br />
sources on regional air quality.<br />
References<br />
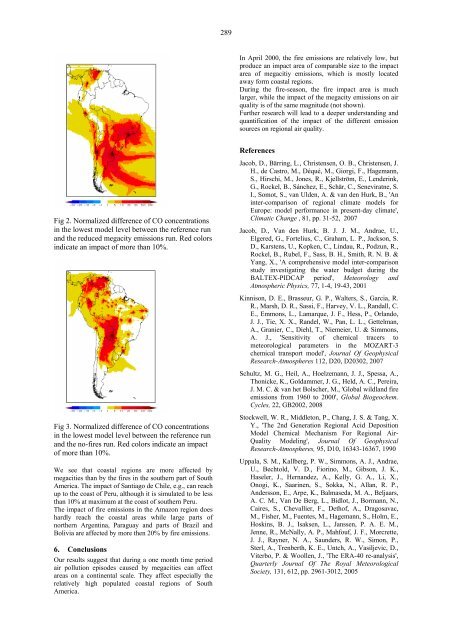
Fig 2. Normalized difference of CO concentrations<br />
in the lowest model level between the reference run<br />
and the reduced megacity emissions run. Red colors<br />
indicate an impact of more than 10%.<br />
Jacob, D., Bärring, L., Christensen, O. B., Christensen, J.<br />
H., de Castro, M., Déqué, M., Giorgi, F., Hagemann,<br />
S., Hirschi, M., Jones, R., Kjellström, E., Lenderink,<br />
G., Rockel, B., Sánchez, E., Schär, C., Seneviratne, S.<br />
I., Somot, S., van Ulden, A. & van den Hurk, B., 'An<br />
inter-comparison of regional climate models for<br />
Europe: model performance in present-day climate',<br />
Climatic Change , 81, pp. 31-52, 2007<br />
Jacob, D., Van den Hurk, B. J. J. M., Andrae, U.,<br />
Elgered, G., Fortelius, C., Graham, L. P., Jackson, S.<br />
D., Karstens, U., Kopken, C., Lindau, R., Podzun, R.,<br />
Rockel, B., Rubel, F., Sass, B. H., Smith, R. N. B. &<br />
Yang, X., 'A comprehensive model inter-comparison<br />
study investigating the water budget during the<br />
<strong>BALTEX</strong>-PIDCAP period', Meteorology and<br />
Atmospheric Physics, 77, 1-4, 19-43, 2001<br />
Kinnison, D. E., Brasseur, G. P., Walters, S., Garcia, R.<br />
R., Marsh, D. R., Sassi, F., Harvey, V. L., Randall, C.<br />
E., Emmons, L., Lamarque, J. F., Hess, P., Orlando,<br />
J. J., Tie, X. X., Randel, W., Pan, L. L., Gettelman,<br />
A., Granier, C., Diehl, T., Niemeier, U. & Simmons,<br />
A. J., 'Sensitivity of chemical tracers to<br />
meteorological parameters in the MOZART-3<br />
chemical transport model', Journal Of Geophysical<br />
Research-Atmospheres 112, D20, D20302, 2007<br />
Schultz, M. G., Heil, A., Hoelzemann, J. J., Spessa, A.,<br />
Thonicke, K., Goldammer, J. G., Held, A. C., Pereira,<br />
J. M. C. & van het Bolscher, M., 'Global wildland fire<br />
emissions from 1960 to 2000', Global Biogeochem.<br />
Cycles, 22, GB2002, 2008<br />
Fig 3. Normalized difference of CO concentrations<br />
in the lowest model level between the reference run<br />
and the no-fires run. Red colors indicate an impact<br />
of more than 10%.<br />
We see that coastal regions are more affected by<br />
megacities than by the fires in the southern part of South<br />
America. The impact of Santiago de Chile, e.g., can reach<br />
up to the coast of Peru, although it is simulated to be less<br />
than 10% at maximum at the coast of southern Peru.<br />
The impact of fire emissions in the Amazon region does<br />
hardly reach the coastal areas while large parts of<br />
northern Argentina, Paraguay and parts of Brazil and<br />
Bolivia are affected by more then 20% by fire emissions.<br />
6. Conclusions<br />
Our results suggest that during a one month time period<br />
air pollution episodes caused by megacities can affect<br />
areas on a continental scale. They affect especially the<br />
relatively high populated coastal regions of South<br />
America.<br />
Stockwell, W. R., Middleton, P., Chang, J. S. & Tang, X.<br />
Y., 'The 2nd Generation Regional Acid Deposition<br />
Model Chemical Mechanism For Regional Air-<br />
<strong>Quality</strong> Modeling', Journal Of Geophysical<br />
Research-Atmospheres, 95, D10, 16343-16367, 1990<br />
Uppala, S. M., Kallberg, P. W., Simmons, A. J., Andrae,<br />
U., Bechtold, V. D., Fiorino, M., Gibson, J. K.,<br />
Haseler, J., Hernandez, A., Kelly, G. A., Li, X.,<br />
Onogi, K., Saarinen, S., Sokka, N., Allan, R. P.,<br />
Andersson, E., Arpe, K., Balmaseda, M. A., Beljaars,<br />
A. C. M., Van De Berg, L., Bidlot, J., Bormann, N.,<br />
Caires, S., Chevallier, F., Dethof, A., Dragosavac,<br />
M., Fisher, M., Fuentes, M., Hagemann, S., Holm, E.,<br />
Hoskins, B. J., Isaksen, L., Janssen, P. A. E. M.,<br />
Jenne, R., McNally, A. P., Mahfouf, J. F., Morcrette,<br />
J. J., Rayner, N. A., Saunders, R. W., Simon, P.,<br />
Sterl, A., Trenberth, K. E., Untch, A., Vasiljevic, D.,<br />
Viterbo, P. & Woollen, J., 'The ERA-40 re-analysis',<br />
Quarterly Journal Of The Royal Meteorological<br />
Society, 131, 612, pp. 2961-3012, 2005