Economic Assessment of Sanitation Interventions in Vietnam - WSP
Economic Assessment of Sanitation Interventions in Vietnam - WSP
Economic Assessment of Sanitation Interventions in Vietnam - WSP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
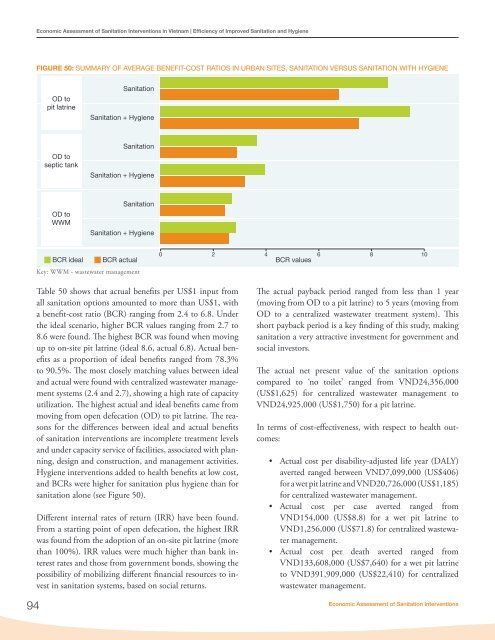
<strong>Economic</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Sanitation</strong> <strong>Interventions</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Vietnam</strong> | Efficiency <strong>of</strong> Improved <strong>Sanitation</strong> and HygieneFIGURE 50: SUMMARY OF AVERAGE BENEFIT-COST RATIOS IN URBAN SITES, SANITATION VERSUS SANITATION WITH HYGIENEOD topit latr<strong>in</strong>e<strong>Sanitation</strong><strong>Sanitation</strong> + HygieneOD toseptic tank<strong>Sanitation</strong><strong>Sanitation</strong> + HygieneOD toWWM<strong>Sanitation</strong><strong>Sanitation</strong> + HygieneBCR idealBCR actualKey: WWM - wastewater management0 2 4 6 8 10BCR values94Table 50 shows that actual benefits per US$1 <strong>in</strong>put fromall sanitation options amounted to more than US$1, witha benefit-cost ratio (BCR) rang<strong>in</strong>g from 2.4 to 6.8. Underthe ideal scenario, higher BCR values rang<strong>in</strong>g from 2.7 to8.6 were found. The highest BCR was found when mov<strong>in</strong>gup to on-site pit latr<strong>in</strong>e (ideal 8.6, actual 6.8). Actual benefitsas a proportion <strong>of</strong> ideal benefits ranged from 78.3%to 90.5%. The most closely match<strong>in</strong>g values between idealand actual were found with centralized wastewater managementsystems (2.4 and 2.7), show<strong>in</strong>g a high rate <strong>of</strong> capacityutilization. The highest actual and ideal benefits came frommov<strong>in</strong>g from open defecation (OD) to pit latr<strong>in</strong>e. The reasonsfor the differences between ideal and actual benefits<strong>of</strong> sanitation <strong>in</strong>terventions are <strong>in</strong>complete treatment levelsand under capacity service <strong>of</strong> facilities, associated with plann<strong>in</strong>g,design and construction, and management activities.Hygiene <strong>in</strong>terventions added to health benefits at low cost,and BCRs were higher for sanitation plus hygiene than forsanitation alone (see Figure 50).Different <strong>in</strong>ternal rates <strong>of</strong> return (IRR) have been found.From a start<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> open defecation, the highest IRRwas found from the adoption <strong>of</strong> an on-site pit latr<strong>in</strong>e (morethan 100%). IRR values were much higher than bank <strong>in</strong>terestrates and those from government bonds, show<strong>in</strong>g thepossibility <strong>of</strong> mobiliz<strong>in</strong>g different f<strong>in</strong>ancial resources to <strong>in</strong>vest<strong>in</strong> sanitation systems, based on social returns.The actual payback period ranged from less than 1 year(mov<strong>in</strong>g from OD to a pit latr<strong>in</strong>e) to 5 years (mov<strong>in</strong>g fromOD to a centralized wastewater treatment system). Thisshort payback period is a key f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> this study, mak<strong>in</strong>gsanitation a very attractive <strong>in</strong>vestment for government andsocial <strong>in</strong>vestors.The actual net present value <strong>of</strong> the sanitation optionscompared to ‘no toilet’ ranged from VND24,356,000(US$1,625) for centralized wastewater management toVND24,925,000 (US$1,750) for a pit latr<strong>in</strong>e.In terms <strong>of</strong> cost-effectiveness, with respect to health outcomes:• Actual cost per disability-adjusted life year (DALY)averted ranged between VND7,099,000 (US$406)for a wet pit latr<strong>in</strong>e and VND20,726,000 (US$1,185)for centralized wastewater management.• Actual cost per case averted ranged fromVND154,000 (US$8.8) for a wet pit latr<strong>in</strong>e toVND1,256,000 (US$71.8) for centralized wastewatermanagement.• Actual cost per death averted ranged fromVND133,608,000 (US$7,640) for a wet pit latr<strong>in</strong>eto VND391,909,000 (US$22,410) for centralizedwastewater management.<strong>Economic</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Sanitation</strong> <strong>Interventions</strong>