1 Surgery CAMLOG Compendium
1 Surgery CAMLOG Compendium
1 Surgery CAMLOG Compendium
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Planning<br />
General Information<br />
Radiographic Evaluation<br />
Dental x-rays<br />
Dental x-rays are sufficient for the initial<br />
assessment of bone supply with single<br />
tooth gaps or small interdental gaps. The<br />
periodontic situation of the remaining<br />
dentition must be closely examined,<br />
because the implant site may be colonized<br />
by pathogenic organisms from<br />
infected pockets.<br />
Orthopantomograph<br />
An OPG is a critical instrument for gathering<br />
basic information. Additional data<br />
required by the specific situation may be<br />
obtained through dental x-rays, remote<br />
x-ray side views, or computer-tomographic<br />
scans (CT).<br />
Remote x-ray side View<br />
Use for large sagittal differences and<br />
planned bone removal in the chin<br />
region.<br />
Computer-Tomographic Scan<br />
The CT is an instrument to be used for<br />
extensive radiological diagnostics. It<br />
enables a 3-D evaluation of the site<br />
from its anatomical structures and the<br />
planning of augmentations. Indications<br />
must be strictly adhered to because of<br />
the level of radiation exposure involved.<br />
22<br />
Laboratory<br />
Cast Analysis<br />
It is essential to mount a diagnostic cast<br />
in an adjustable articulator to assess jaw<br />
relations. Specifically, a check should be<br />
made whether a change of the<br />
occlusal position is worthwhile or<br />
required. If at all possible, it should be<br />
done before the actual implant-supported<br />
prosthetic treatment gets under way.<br />
In any case, a change in occlusal height<br />
must be preceded by treatment with a<br />
long-term provisional.<br />
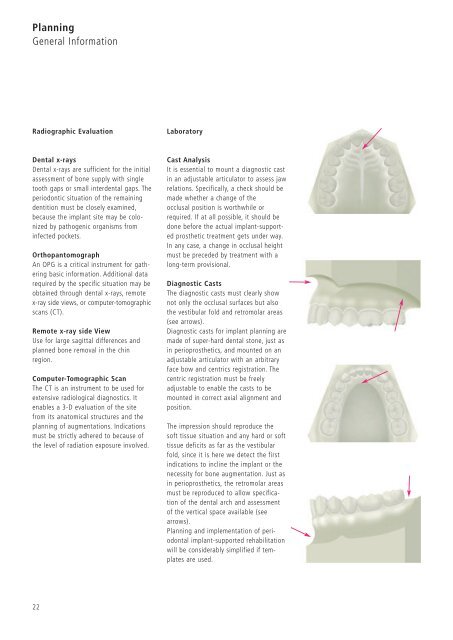
Diagnostic Casts<br />
The diagnostic casts must clearly show<br />
not only the occlusal surfaces but also<br />
the vestibular fold and retromolar areas<br />
(see arrows).<br />
Diagnostic casts for implant planning are<br />
made of super-hard dental stone, just as<br />
in perioprosthetics, and mounted on an<br />
adjustable articulator with an arbitrary<br />
face bow and centrics registration. The<br />
centric registration must be freely<br />
adjustable to enable the casts to be<br />
mounted in correct axial alignment and<br />
position.<br />
The impression should reproduce the<br />
soft tissue situation and any hard or soft<br />
tissue deficits as far as the vestibular<br />
fold, since it is here we detect the first<br />
indications to incline the implant or the<br />
necessity for bone augmentation. Just as<br />
in perioprosthetics, the retromolar areas<br />
must be reproduced to allow specification<br />
of the dental arch and assessment<br />
of the vertical space available (see<br />
arrows).<br />
Planning and implementation of periodontal<br />
implant-supported rehabilitation<br />
will be considerably simplified if templates<br />
are used.