Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
= 4<br />
3 π(3r2 )<br />
= 4πr 2 expresión que correspon<strong>de</strong> precisamente al área <strong>de</strong> la superficie <strong>de</strong> la esfera.<br />
Diferenciales<br />
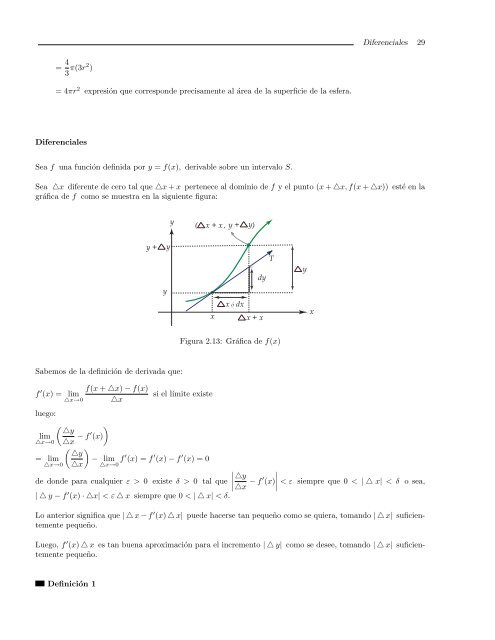
Sea f <strong>una</strong> <strong>función</strong> <strong>de</strong>finida por y = f(x), <strong>de</strong>rivable sobre un intervalo S.<br />
Diferenciales 29<br />
Sea △x diferente <strong>de</strong> cero tal que △x + x pertenece al dominio <strong>de</strong> f y el punto (x + △x, f(x + △x)) esté en la<br />
gráfica <strong>de</strong> f como se muestra en la siguiente figura:<br />
Sabemos <strong>de</strong> la <strong>de</strong>finición <strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong>rivada que:<br />
f ′ f(x + △x) − f(x)<br />
(x) = lim<br />
△x→0 △x<br />
Figura 2.13: Gráfica <strong>de</strong> f(x)<br />
si el límite existe<br />
luego:<br />
<br />
△y<br />
lim<br />
△x→0 △x − f ′ <br />
(x)<br />
<br />
△y<br />
= lim − lim<br />
△x→0 △x △x→0 f ′ (x) = f ′ (x) − f ′ (x) = 0<br />
<br />
<br />
<strong>de</strong> don<strong>de</strong> para cualquier ε > 0 existe δ > 0 tal que <br />
△y<br />
△x<br />
− f ′ <br />
<br />
(x) <br />
< ε siempre que 0 < | △ x| < δ o sea,<br />
| △ y − f ′ (x) · △x| < ε △ x siempre que 0 < | △ x| < δ.<br />
Lo anterior significa que | △ x − f ′ (x) △ x| pue<strong>de</strong> hacerse tan pequeño como se quiera, tomando | △ x| suficientemente<br />
pequeño.<br />
Luego, f ′ (x) △ x es tan buena aproximación para el incremento | △ y| como se <strong>de</strong>see, tomando | △ x| suficientemente<br />
pequeño.<br />
Definición 1<br />
_<br />
_