Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
70 Capítulo 2: <strong>Derivada</strong>s<br />
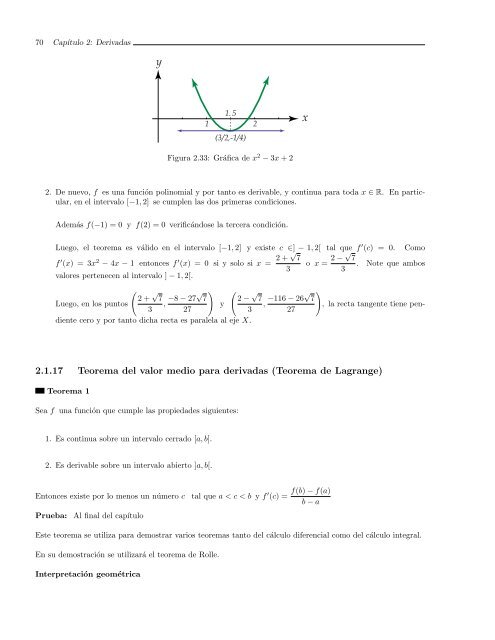
Figura 2.33: Gráfica <strong>de</strong> x 2 − 3x + 2<br />
2. De nuevo, f es <strong>una</strong> <strong>función</strong> polinomial y por tanto es <strong>de</strong>rivable, y continua para toda x ∈ R. En particular,<br />
en el intervalo [−1, 2] se cumplen las dos primeras condiciones.<br />
A<strong>de</strong>más f(−1) = 0 y f(2) = 0 verificándose la tercera condición.<br />
Luego, el teorema es válido en el intervalo [−1, 2] y existe c ∈] − 1, 2[ tal que f ′ (c) = 0. Como<br />
f ′ (x) = 3x2 − 4x − 1 entonces f ′ (x) = 0 si y solo si x = 2 + √ 7<br />
o x =<br />
3<br />
2 − √ 7<br />
. Note que ambos<br />
3<br />
valores pertenecen al intervalo ] − 1, 2[.<br />
<br />
2 +<br />
Luego, en los puntos<br />
√ 7<br />
,<br />
3<br />
−8 − 27√ <br />
7<br />
27<br />
y<br />
<br />
2 − √ 7<br />
,<br />
3<br />
−116 − 26√ <br />
7<br />
, la recta tangente tiene pen-<br />
27<br />
diente cero y por tanto dicha recta es paralela al eje X.<br />
2.1.17 Teorema <strong>de</strong>l valor medio para <strong>de</strong>rivadas (Teorema <strong>de</strong> Lagrange)<br />
Teorema 1<br />
Sea f <strong>una</strong> <strong>función</strong> que cumple las propieda<strong>de</strong>s siguientes:<br />
1. Es continua sobre un intervalo cerrado [a, b].<br />
2. Es <strong>de</strong>rivable sobre un intervalo abierto ]a, b[.<br />
Entonces existe por lo menos un número c tal que a < c < b y f ′ (c) =<br />
Prueba: Al final <strong>de</strong>l capítulo<br />
f(b) − f(a)<br />
b − a<br />
Este teorema se utiliza para <strong>de</strong>mostrar varios teoremas tanto <strong>de</strong>l cálculo diferencial como <strong>de</strong>l cálculo integral.<br />
En su <strong>de</strong>mostración se utilizará el teorema <strong>de</strong> Rolle.<br />
Interpretación geométrica