Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ejercicios.<br />
Determine D 2 xy y exprese el resultado en la forma más simplificada posible.<br />
a. x 2 − 2y 2 = 4<br />
b. x 2<br />
3 + y 2<br />
3 = a 2<br />
3 a cte.<br />
c. b 2 x 2 − a 2 y 2 = a 2 b 2 a cte, b cte.<br />
2.1.16 Teorema <strong>de</strong> Rolle (o teorema sobre las raíces <strong>de</strong> la <strong>de</strong>rivada)<br />
Teorema 1<br />
Sea f <strong>una</strong> <strong>función</strong> que cumple las condiciones siguientes:<br />
1. f es continua sobre un intervalo cerrado [a, b].<br />
2. f es <strong>de</strong>rivable sobre un intervalo abierto ]a, b[.<br />
3. f(a) = f(b) = 0.<br />
Teorema <strong>de</strong> Rolle 67<br />
Entonces existe por lo menos un número real c tal que a < c < b y f ′ (c) = 0. O sea f ′ (x) = 0 para cierto<br />
c entre a y b.<br />
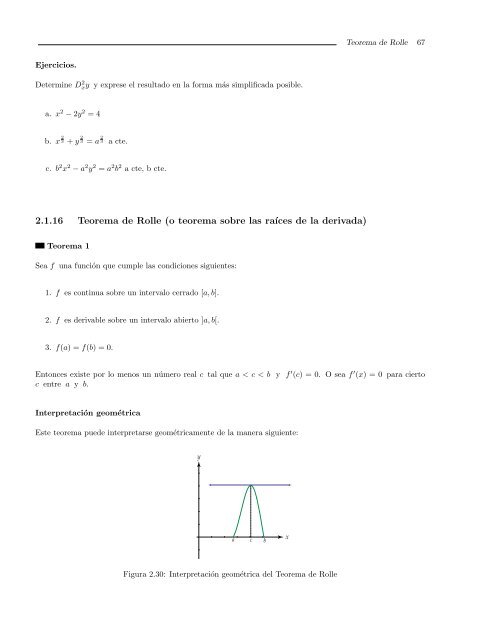
Interpretación geométrica<br />
Este teorema pue<strong>de</strong> interpretarse geométricamente <strong>de</strong> la manera siguiente:<br />
Figura 2.30: Interpretación geométrica <strong>de</strong>l Teorema <strong>de</strong> Rolle