Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Las funciones trigonométricas inversas y sus <strong>de</strong>rivadas 51<br />
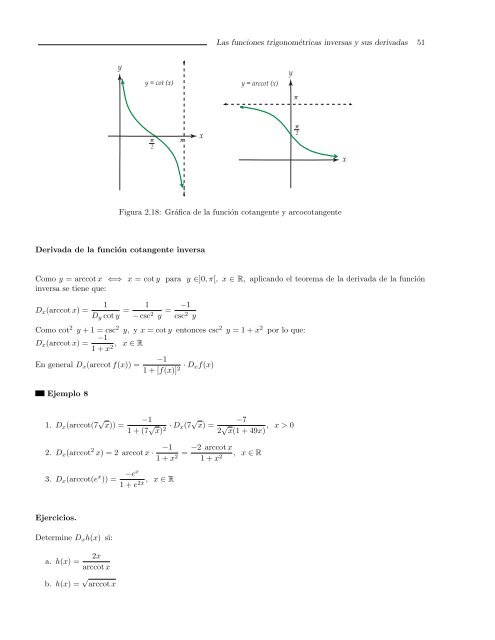
Figura 2.18: Gráfica <strong>de</strong> la <strong>función</strong> cotangente y arcocotangente<br />
<strong>Derivada</strong> <strong>de</strong> la <strong>función</strong> cotangente inversa<br />
Como y = arccot x ⇐⇒ x = cot y para y ∈]0, π[, x ∈ R, aplicando el teorema <strong>de</strong> la <strong>de</strong>rivada <strong>de</strong> la <strong>función</strong><br />
inversa se tiene que:<br />
Dx(arccot x) =<br />
1<br />
Dy cot y =<br />
1<br />
− csc2 −1<br />
=<br />
y csc2 y<br />
Como cot 2 y + 1 = csc 2 y, y x = cot y entonces csc 2 y = 1 + x 2 por lo que:<br />
Dx(arccot x) = −1<br />
, x ∈ R<br />
1 + x2 −1<br />
En general Dx(arccot f(x)) =<br />
· Dxf(x)<br />
1 + [f(x)] 2<br />
Ejemplo 8<br />
1. Dx(arccot(7 √ x)) =<br />
−1<br />
1 + (7 √ x) 2 · Dx(7 √ −7<br />
x) =<br />
2 √ , x > 0<br />
x(1 + 49x)<br />
2. Dx(arccot 2 x) = 2 arccot x · −1 −2 arccot x<br />
=<br />
1 + x2 1 + x2 , x ∈ R<br />
3. Dx(arccot(e x )) = −ex<br />
, x ∈ R<br />
1 + e2x Ejercicios.<br />
Determine Dxh(x) si:<br />
a. h(x) =<br />
2x<br />
arccot x<br />
b. h(x) = √ arccot x