Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
Derivada de una función - TEC-Digital
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Q pue<strong>de</strong> expresarse entonces como:<br />
Ejemplo 4<br />
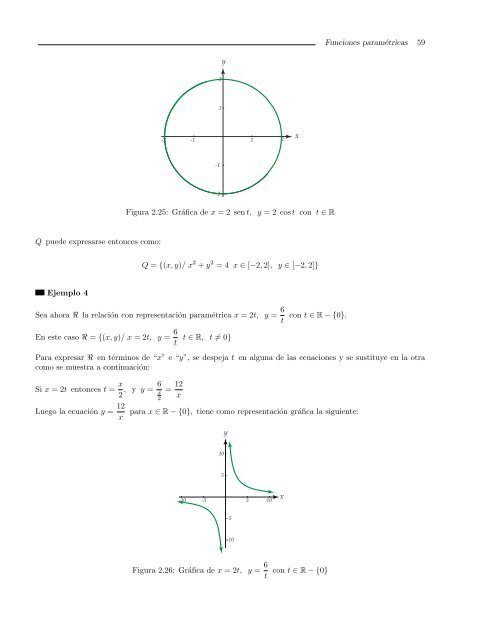
Figura 2.25: Gráfica <strong>de</strong> x = 2 sen t, y = 2 cos t con t ∈ R<br />
Q = {(x, y)/ x 2 + y 2 = 4 x ∈ [−2, 2], y ∈ [−2, 2]}<br />
Sea ahora ℜ la relación con representación paramétrica x = 2t, y = 6<br />
t<br />
En este caso ℜ = {(x, y)/ x = 2t, y = 6<br />
t ∈ R, t = 0}<br />
t<br />
con t ∈ R − {0}.<br />
Funciones paramétricas 59<br />
Para expresar ℜ en términos <strong>de</strong> “x” e “y”, se <strong>de</strong>speja t en alg<strong>una</strong> <strong>de</strong> las ecuaciones y se sustituye en la otra<br />
como se muestra a continuación:<br />
Si x = 2t entonces t = x<br />
2 , y y = 6 x<br />
2<br />
Luego la ecuación y = 12<br />
x<br />
= 12<br />
x<br />
para x ∈ R − {0}, tiene como representación gráfica la siguiente:<br />
Figura 2.26: Gráfica <strong>de</strong> x = 2t, y = 6<br />
t<br />
con t ∈ R − {0}