Méthodes de Monte Carlo appliquées au pricing d ... - Maths-fi.com
Méthodes de Monte Carlo appliquées au pricing d ... - Maths-fi.com
Méthodes de Monte Carlo appliquées au pricing d ... - Maths-fi.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
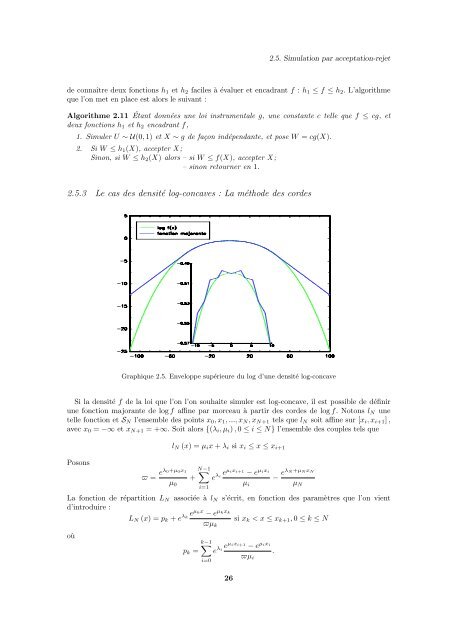
2.5. Simulation par acceptation-rejet<strong>de</strong> connaître <strong>de</strong>ux fonctions h 1 et h 2 faciles à évaluer et encadrant f : h 1 ≤ f ≤ h 2 . L’algorithmeque l’on met en place est alors le suivant :Algorithme 2.11 Étant données une loi instrumentale g, une constante c telle que f ≤ cg, et<strong>de</strong>ux fonctions h 1 et h 2 encadrant f,1. Simuler U ∼ U(0, 1) et X ∼ g <strong>de</strong> façon indépendante, et pose W = cg(X).2. Si W ≤ h 1 (X), accepter X ;Sinon, si W ≤ h 2 (X) alors – si W ≤ f(X), accepter X ;– sinon retourner en 1.2.5.3 Le cas <strong>de</strong>s <strong>de</strong>nsité log-concaves : La métho<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong>s cor<strong>de</strong>sGraphique 2.5. Enveloppe supérieure du log d’une <strong>de</strong>nsité log-concaveSi la <strong>de</strong>nsité f <strong>de</strong> la loi que l’on l’on souhaite simuler est log-concave, il est possible <strong>de</strong> dé<strong>fi</strong>nirune fonction majorante <strong>de</strong> log f af<strong>fi</strong>ne par morce<strong>au</strong> à partir <strong>de</strong>s cor<strong>de</strong>s <strong>de</strong> log f. Notons l N unetelle fonction et S N l’ensemble <strong>de</strong>s points x 0 , x 1 , ..., x N , x N+1 tels que l N soit af<strong>fi</strong>ne sur [x i , x i+1 ] ,avec x 0 = −∞ et x N+1 = +∞. Soit alors {(λ i , µ i ) , 0 ≤ i ≤ N} l’ensemble <strong>de</strong>s couples tels quePosonsl N (x) = µ i x + λ i si x i ≤ x ≤ x i+1N−1∑ − eϖ = eλ0+µ0x1+ e λi eµixi+1 µixi− eλ N +µ N x Nµ 0 µ i µ Ni=1La fonction <strong>de</strong> répartition L N associée à l N s’écrit, en fonction <strong>de</strong>s paramètres que l’on vientd’introduire :L N (x) = p k + e λ eµ kx − e µ kx kkϖµ ksi x k < x ≤ x k+1 , 0 ≤ k ≤ Noùk−1∑ − ep k = e λi eµixi+1 µixi.ϖµ ii=026