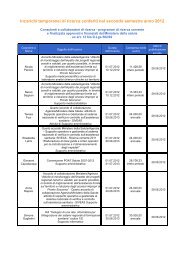
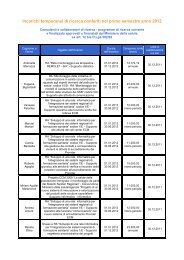
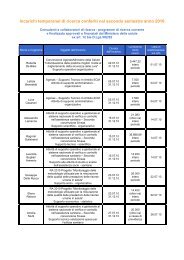
dolore paziente pediatrico - Age.Na.S.
dolore paziente pediatrico - Age.Na.S.
dolore paziente pediatrico - Age.Na.S.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
114 Bibliografia<br />
tal pain, agitation and sedation scale with prolonged pain. J Perinatol 2008; 28: 55-60.<br />
Hummel P, van Dijk M. Pain assessment: current status and challenges. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med<br />
2006; 11: 237-45.<br />
Lawrence J, Alcock D, McGrath P, et al. The development of a tool to assess neonatal pain. Neonatal<br />
Netw 1993; 12: 59-66.<br />
Merkel SI, Voepel-Lewis T, Shayevitz JR, Malviya S. The FLACC: a behavioral scale for scoring postoperative<br />
pain in young children. Pediatr Nurs 1997; 23: 293-7.<br />
Ranger M, Johnston CC, Anand KJ. Current controversies regarding pain assessment in neonates.<br />
Semin Perinatol 2007; 31: 283-8.<br />
Stevens B, Johnston C, Petryshen P, Taddio A. Premature infant pain profile: development and initial<br />
validation. Clin J Pain 1996; 12: 13-22.<br />
Voepel-Lewis T, Malviya S, Tait AR. Validity of parent ratings as proxy measures of pain in children with<br />
cognitive impairment. Pain Manag Nurs 2005; 6: 168-74.<br />
Wong D, Baker C. Pain in children: comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr Nurs 1988; 14: 9-17.<br />
Capitolo 5<br />
Barbi E, Cantoni L, Panizon F. Medico e Bambino. Prontuario Pediatrico. Guida alla terapia. VI ed.<br />
Milano: Edifarm, 2004.<br />
Barbi E, Marchetti F. Il bambino e il <strong>dolore</strong>. Pediatria pronta per l’uso. Pisa: Primula Multimedia srl,<br />
2006.<br />
Bernstein RM, Cozen H. Evaluation of back pain in children and adolescents. Am Fam Physician 2007;<br />
76: 1669-76.<br />
Breau LM, Camfield CS, McGrath PJ, Finley GA. The incidence of pain in children with severe cognitive<br />
impairment. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2003; 157: 1219-26.<br />
Clinch J, Eccleston C. Chronic musculoskeletal pain in children: assessment and management. Rheumatology<br />
(Oxford) 2009; 48: 466-74.<br />
Fortier MA, Chorney JM, Rony RY, et al. Children’s desire for perioperative information. Anesth Analg<br />
2009; 109: 1085-90.<br />
Noe JD, Li BU. <strong>Na</strong>vigating recurrent abdominal pain through clinical clues, red flags and initial testing.<br />
Pediatr Ann 2009; 38: 259-66.<br />
Capitolo 6<br />
Anand KJ; International Evidence-Based Group for Neonatal Pain. Consensus statement for the prevention<br />
and management of pain in the newborn. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2001; 155: 173-80.<br />
Broome ME, Endsley RC. Group preparation of young children for painful stimulus. West J Nurs Res<br />
1987; 9: 484-502.<br />
Caty S, Ellerton ML, Ritchie JA. Use of a projective technique to assess young children’s appraisal and<br />
coping responses to a venipuncture. J Soc Pediatr Nurs 1997; 2: 83-92.<br />
Chen E, Joseph MH, Zeltzer LK. Behavioral and cognitive interventions in the treatment of pain in<br />
children. Pediatr Clin North Am 2000; 47: 513-25.<br />
Cignacco E, Hamers JP, Stoffel L, et al. The efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions in the<br />
management of procedural pain in preterm and term neonates. A systematic literature review. Eur<br />
J Pain 2007; 11: 139-52.<br />
Golianu B, Krane E, Seybold J, et al. Non-pharmacological techniques for pain management in neo-