Nanotechnologie in Lebensmitteln - DLR Online: Deutsche ...
Nanotechnologie in Lebensmitteln - DLR Online: Deutsche ...
Nanotechnologie in Lebensmitteln - DLR Online: Deutsche ...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
44<br />
Area<br />
6000<br />
5000<br />
4000<br />
3000<br />
2000<br />
1000<br />
0<br />
Orig<strong>in</strong>alarbeiten «<br />
5 20 40 60 80<br />
Extraction time [m<strong>in</strong>]<br />
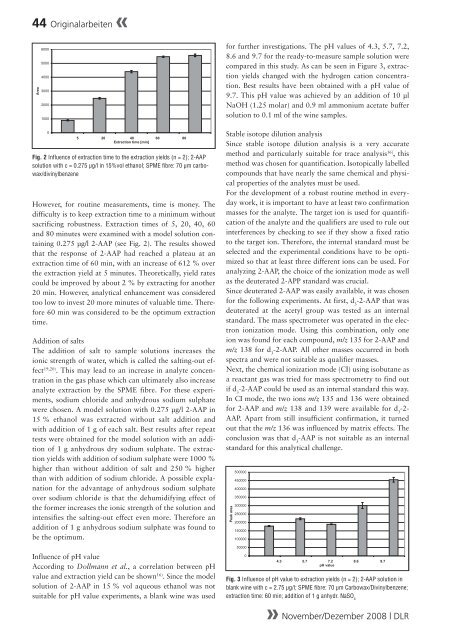
Fig. 2 Influence of extraction time to the extraction yields (n = 2); 2-AAP<br />
solution with c = 0.275 µg/l <strong>in</strong> 15%vol ethanol; SPME fibre: 70 µm carbowax/div<strong>in</strong>ylbenzene<br />
However, for rout<strong>in</strong>e measurements, time is money. The<br />
difficulty is to keep extraction time to a m<strong>in</strong>imum without<br />
sacrific<strong>in</strong>g robustness. Extraction times of 5, 20, 40, 60<br />
and 80 m<strong>in</strong>utes were exam<strong>in</strong>ed with a model solution conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
0.275 μg/l 2-AAP (see Fig. 2). The results showed<br />
that the response of 2-AAP had reached a plateau at an<br />
extraction time of 60 m<strong>in</strong>, with an <strong>in</strong>crease of 612 % over<br />
the extraction yield at 5 m<strong>in</strong>utes. Theoretically, yield rates<br />
could be improved by about 2 % by extract<strong>in</strong>g for another<br />
20 m<strong>in</strong>. However, analytical enhancement was considered<br />
too low to <strong>in</strong>vest 20 more m<strong>in</strong>utes of valuable time. Therefore<br />
60 m<strong>in</strong> was considered to be the optimum extraction<br />
time.<br />
Addition of salts<br />
The addition of salt to sample solutions <strong>in</strong>creases the<br />
ionic strength of water, which is called the salt<strong>in</strong>g-out effect<br />
19,20) . This may lead to an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> analyte concentration<br />
<strong>in</strong> the gas phase which can ultimately also <strong>in</strong>crease<br />
analyte extraction by the SPME fibre. For these experiments,<br />
sodium chloride and anhydrous sodium sulphate<br />
were chosen. A model solution with 0.275 μg/l 2-AAP <strong>in</strong><br />
15 % ethanol was extracted without salt addition and<br />
with addition of 1 g of each salt. Best results after repeat<br />
tests were obta<strong>in</strong>ed for the model solution with an addition<br />
of 1 g anhydrous dry sodium sulphate. The extraction<br />
yields with addition of sodium sulphate were 1000 %<br />
higher than without addition of salt and 250 % higher<br />
than with addition of sodium chloride. A possible explanation<br />
for the advantage of anhydrous sodium sulphate<br />
over sodium chloride is that the dehumidify<strong>in</strong>g effect of<br />
the former <strong>in</strong>creases the ionic strength of the solution and<br />
<strong>in</strong>tensifies the salt<strong>in</strong>g-out effect even more. Therefore an<br />
addition of 1 g anhydrous sodium sulphate was found to<br />
be the optimum.<br />
Influence of pH value<br />
Accord<strong>in</strong>g to Dollmann et al., a correlation between pH<br />
value and extraction yield can be shown 16) . S<strong>in</strong>ce the model<br />
solution of 2-AAP <strong>in</strong> 15 % vol aqueous ethanol was not<br />
suitable for pH value experiments, a blank w<strong>in</strong>e was used<br />
for further <strong>in</strong>vestigations. The pH values of 4.3, 5.7, 7.2,<br />
8.6 and 9.7 for the ready-to-measure sample solution were<br />
compared <strong>in</strong> this study. As can be seen <strong>in</strong> Figure 3, extraction<br />
yields changed with the hydrogen cation concentration.<br />
Best results have been obta<strong>in</strong>ed with a pH value of<br />
9.7. This pH value was achieved by an addition of 10 μl<br />
NaOH (1.25 molar) and 0.9 ml ammonium acetate buffer<br />
solution to 0.1 ml of the w<strong>in</strong>e samples.<br />
Stable isotope dilution analysis<br />
S<strong>in</strong>ce stable isotope dilution analysis is a very accurate<br />
method and particularly suitable for trace analysis 16) , this<br />
method was chosen for quantification. Isotopically labelled<br />
compounds that have nearly the same chemical and physical<br />
properties of the analytes must be used.<br />
For the development of a robust rout<strong>in</strong>e method <strong>in</strong> everyday<br />
work, it is important to have at least two confirmation<br />
masses for the analyte. The target ion is used for quantification<br />
of the analyte and the qualifiers are used to rule out<br />
<strong>in</strong>terferences by check<strong>in</strong>g to see if they show a fixed ratio<br />
to the target ion. Therefore, the <strong>in</strong>ternal standard must be<br />
selected and the experimental conditions have to be optimized<br />
so that at least three different ions can be used. For<br />
analyz<strong>in</strong>g 2-AAP, the choice of the ionization mode as well<br />
as the deuterated 2-APP standard was crucial.<br />
S<strong>in</strong>ce deuterated 2-AAP was easily available, it was chosen<br />
for the follow<strong>in</strong>g experiments. At first, d 3 -2-AAP that was<br />
deuterated at the acetyl group was tested as an <strong>in</strong>ternal<br />
standard. The mass spectrometer was operated <strong>in</strong> the electron<br />
ionization mode. Us<strong>in</strong>g this comb<strong>in</strong>ation, only one<br />
ion was found for each compound, m/z 135 for 2-AAP and<br />
m/z 138 for d 3 -2-AAP. All other masses occurred <strong>in</strong> both<br />
spectra and were not suitable as qualifier masses.<br />
Next, the chemical ionization mode (CI) us<strong>in</strong>g isobutane as<br />
a reactant gas was tried for mass spectrometry to f<strong>in</strong>d out<br />
if d 3 -2-AAP could be used as an <strong>in</strong>ternal standard this way.<br />
In CI mode, the two ions m/z 135 and 136 were obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
for 2-AAP and m/z 138 and 139 were available for d 3 -2-<br />
AAP. Apart from still <strong>in</strong>sufficient confirmation, it turned<br />
out that the m/z 136 was <strong>in</strong>fluenced by matrix effects. The<br />
conclusion was that d 3 -AAP is not suitable as an <strong>in</strong>ternal<br />
standard for this analytical challenge.<br />
Peak area<br />
500000<br />
450000<br />
400000<br />
350000<br />
300000<br />
250000<br />
200000<br />
150000<br />
100000<br />
50000<br />
0<br />
4.3 5.7 7.2 8.6 9.7<br />
pH value<br />
Fig. 3 Influence of pH value to extraction yields (n = 2); 2-AAP solution <strong>in</strong><br />
blank w<strong>in</strong>e with c = 2.75 µg/l; SPME fibre: 70 µm Carbowax/Div<strong>in</strong>ylbenzene;<br />
extraction time: 60 m<strong>in</strong>; addition of 1 g anhydr. NaSO 4<br />
» November/Dezember 2008 | <strong>DLR</strong>