Space Security Index
Space Security Index
Space Security Index
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Space</strong> <strong>Security</strong> 2011<br />
32<br />
On 13 October, a Russian Breeze-M upper stage (object 2008-011B) experienced minor<br />
fragmentation in its geotransfer parking orbit. 32 e launch vehicle had suered a malfunction<br />
during the 1998 launch of the AMC-14 satellite, which provides satellite television services<br />
for Dish Network. Although AMC-14 was able to maneuver on its own into the GEO belt,<br />
the malfunction left the upper stage in a highly elliptical orbit with a signicant amount of<br />
residual propellant, which is usually consumed during launch. e fragmentation resulted<br />
in 10 cataloged pieces of debris, all of which are expected to remain in orbit for decades. 33<br />
However, the high altitude and the Breeze-M’s elliptical orbit make consistent tracking of<br />
small pieces of debris dicult.<br />
On 1 November, the upper stage (object 2010-057B) of a Chinese Long March 3C rocket<br />
experienced a minor fragmentation in its 160 km x 35,780 km highly elliptical geotransfer<br />
orbit. 34 e event appears to have occurred shortly after the rocket separated from its payload,<br />
a Chinese Beidou G4 navigation satellite. Although approximately 50 pieces of debris were<br />
detected by the SSN, as of January 2011, none had been cataloged. 35<br />
On 24 November, a defunct U.S. NOAA weather satellite (object 1988-089A) experienced<br />
minor fragmentation in its 835 km x 850 km LEO orbit. 36 Five pieces of debris have been<br />
cataloged from this event. 37 ree previous NOAA spacecraft of the same TIROS-N series<br />
have experienced similar fragmentation events, each releasing a few pieces at least a dozen<br />
years after launch, for unknown reasons. 38<br />
On 23 December, a piece of debris (object 2007-005E) from the 2007 launch of the Japanese<br />
IGS 4A and 4B remote sensing satellites experienced a minor fragmentation. 39 e launch<br />
had resulted in the unusually high number of 12 pieces of debris left in orbit, all of which<br />
had decayed in 2007 and 2008, with the exception of object 2007-005E. 40 e SSN initially<br />
detected 10 new pieces of debris from the December 2010 event, cataloging three. 41<br />
A complete listing of the 2010 breakups can be found in Table 1.4 below.<br />
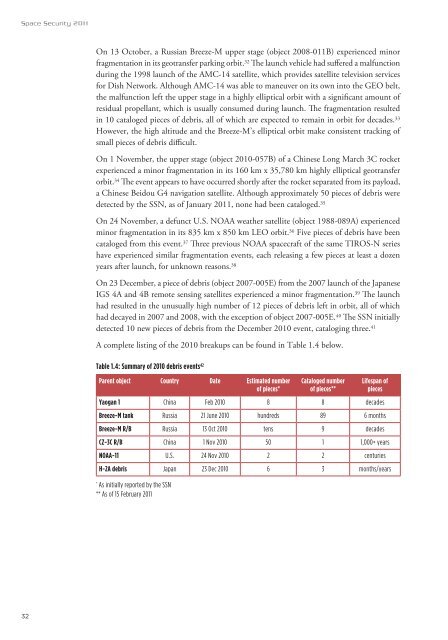
Table 1.4: Summary of 2010 debris events 42<br />
Parent object Country Date Estimated number<br />
of pieces*<br />
Cataloged number<br />
of pieces**<br />
Lifespan of<br />
pieces<br />
Yaogan 1 China Feb 2010 8 8 decades<br />
Breeze-M tank Russia 21 June 2010 hundreds 89 6 months<br />
Breeze-M R/B Russia 13 Oct 2010 tens 9 decades<br />
CZ-3C R/B China 1 Nov 2010 50 1 1,000+ years<br />
NOAA-11 U.S. 24 Nov 2010 2 2 centuries<br />
H-2A debris Japan 23 Dec 2010 6 3 months/years<br />
* As initially reported by the SSN<br />
** As of 15 February 2011