- Page 2 and 3:
Welcome... To Hummert’s New 2018-
- Page 4 and 5:
From The Hummert Team ALL OF US AT
- Page 6 and 7:
insecticides ** INSECTICIDE Hummert
- Page 8 and 9:
insecticides Adept 25 WP Diflubenzu
- Page 10 and 11:
Insecticides insecticides BotaniGar
- Page 12 and 13:
Insecticides insecticides EverGreen
- Page 14 and 15:
Insecticides insecticides Imidaclop
- Page 16 and 17:
insecticides Minx 2 COMPARE TO AVID
- Page 18 and 19:
insecticides PyGanic Gardening Pyre
- Page 20 and 21:
Insecticides insecticides Shuttle O
- Page 22 and 23:
Total Release Products Total Releas
- Page 24 and 25:
premier all natural & organic produ
- Page 26 and 27:
pesticides for the arborist & urban
- Page 28 and 29:
Pesticides for the Arborist & Urban
- Page 30 and 31:
Ready to Use Sticky Cards “A powe
- Page 32 and 33:
Beneficial Insects beneficial insec
- Page 34 and 35:
Beneficial Insects beneficial insec
- Page 36 and 37:
Beneficial Insects How the Orcon Pr
- Page 38 and 39:
insect cages Hummert’s Insect Rea
- Page 40 and 41:
Lawn & Garden Products for Insect C
- Page 42 and 43:
Lawn & Garden Products for Insect C
- Page 44 and 45:
Lawn & Garden Products - Insect Con
- Page 46 and 47:
Two lights generate warmth and UV r
- Page 48 and 49:
Fungicides fungicides Actinovate L&
- Page 50 and 51:
Fungicides fungicides Chipco 26019
- Page 52 and 53:
Fungicides fungicides Headway Azoxy
- Page 54 and 55:
Fungicides fungicides Phyton 35 Cop
- Page 56 and 57:
fungicides SuffOil-X Petroleum Oil
- Page 58 and 59:
Turf Fungicides turf fungicides Dyn
- Page 60 and 61:
Horticultural Products for Disease
- Page 62 and 63:
algaecides • disinfectants BioSaf
- Page 64 and 65:
algaecides • disinfectants SaniDa
- Page 66 and 67:
Air Sanitizers NASA Developed Air S
- Page 68 and 69:
ooting compounds Bontone Rooting Po
- Page 70 and 71:
Plant Growth Regulators plant growt
- Page 72 and 73:
plant growth regulators Cutless 0.3
- Page 74 and 75:
landscape plant growth regulators
- Page 76 and 77:
Hummert’s Helpful Hint: Pre-Emerg
- Page 78 and 79:
pre-emergent herbicides Pre-Emergen
- Page 80 and 81:
pre-emergent herbicides Preen Garde
- Page 82 and 83:
Post-Emergent Herbicides post-emerg
- Page 84 and 85:
post-emergent herbicides Garlon 4 U
- Page 86 and 87:
post-emergent herbicides Razor - Ra
- Page 88 and 89:
post-emergent herbicides Trimec® C
- Page 90 and 91:
Lawn & Garden Products - Weed Kille
- Page 92 and 93:
Aquatic Weed Identification Terrest
- Page 94 and 95:
Aquatic Weed & Algae Identification
- Page 96 and 97:
Aquatic Products aquatic products A
- Page 98 and 99:
Aquatic Weed & Algae Control aquati
- Page 100 and 101:
Powered Air-Purifying Respirator (P
- Page 102 and 103:
Respirators & Replacement Cartridge
- Page 104 and 105:
Spray Suits & Coveralls Saranex Coa
- Page 106 and 107:
Chemical-Resistant Gloves chemical-
- Page 108 and 109:
Sanitation & Skincare Products sani
- Page 110 and 111:
Hummert's ® SUPER SCOOP Now In Neo
- Page 112 and 113:
Simplicity of design and rugged con
- Page 114 and 115:
plastic hand sprayers Plastic Hand
- Page 116 and 117:
Solo & Jacto sprayers 420 Hand Spra
- Page 118 and 119:
Backpack Sprayers Solo backpack spr
- Page 120 and 121:
Electric Backpack Sprayers Why the
- Page 122 and 123:
controlled release fertilizers Huds
- Page 124 and 125:
Horticultural Sprayers controlled r
- Page 126 and 127:
Cannon Sprayers Jacto Cannon spraye
- Page 128 and 129:
Granular Spreaders All VORTEX sprea
- Page 130 and 131:
Horticultural Sprayers • Fully ad
- Page 132 and 133:
Hand-Held and Backpack Sprayers Hud
- Page 134 and 135:
3 Point Sprayer 40 Gallon Premium S
- Page 136 and 137:
Manual & Power Rewind Manual Crank
- Page 138 and 139:
spray guns • nozzles High-Pressur
- Page 140 and 141:
Soil Injectors for Fertilizers & Pe
- Page 142 and 143:
• Dialmatic rate control for accu
- Page 144 and 145:
EarthWay ® Broadcast Spreaders Mod
- Page 146 and 147:
Garden Seeders JP-1 Jang Hand Seede
- Page 148 and 149:
Weed Wipers & Sprayers The Green We
- Page 150 and 151:
hot max torches Big Max Back Pack K
- Page 152 and 153:
Dyna Green grass seed Dyna Green TM
- Page 154 and 155:
How to Read an Analysis Tag Lot # E
- Page 156 and 157:
Hydro Seeding Systems hydro seeding
- Page 158 and 159:
Professional Turf Fertilizers Your
- Page 160 and 161:
GENERAL PURPOSE FERTILIZERS Dyna Gr
- Page 162 and 163:
Professional Granular Turf & Orname
- Page 164 and 165:
For Better Results. Naturally. Natu
- Page 166 and 167:
The Nutrition Solution For Hydropon
- Page 168 and 169: growth products •Little or no sal
- Page 170 and 171: • Build healthy thriving plants,
- Page 172 and 173: Hydroponic Fertilizers hydroponic f
- Page 174 and 175: Baicor fertilizers All Purpose 10-9
- Page 176 and 177: Professional Water- Soluble Fertili
- Page 178 and 179: LX Water-Soluble Fertilizers Jack
- Page 180 and 181: Peters Professional ® • The “O
- Page 182 and 183: Control & Slow Release Fertilizers
- Page 184 and 185: E-Max match RELEASE TECHNOLOGY 1 2
- Page 186 and 187: Give your plant’s root system a b
- Page 188 and 189: Multicote® Precision Release Ferti
- Page 190 and 191: fertilizers Gypsum Pelletized Calci
- Page 192 and 193: Espoma fertilizers Potassium Sulpha
- Page 194 and 195: Espoma fertilizers Since 1929 Alfal
- Page 196 and 197: Fertilizers Espoma fertilizers Sinc
- Page 198 and 199: Fertilizers Jack’s Classic liquid
- Page 200 and 201: Essential Nutrients essential nutri
- Page 202 and 203: Fertilizer Injectors Note: Installa
- Page 204 and 205: Dosatron carts • accessories Eco-
- Page 206 and 207: Dosmatic fertilizer injectors/parts
- Page 208 and 209: Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems Revers
- Page 210 and 211: Storage Tanks & Accessories Five-Ga
- Page 212 and 213: Liquid & Bulk Storage Tanks liquid
- Page 214 and 215: Advanced Horticultural Soil Testing
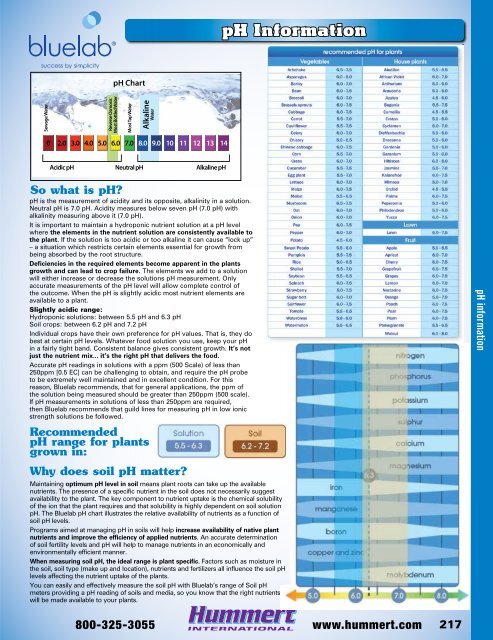
- Page 216 and 217: Soil Testing Instruments Hanna Mode
- Page 220 and 221: Bluelab soil testing instruments Co
- Page 222 and 223: Testing Instrument Cleaning Solutio
- Page 224 and 225: IN-LINE INSTALLATION Grocheck • p
- Page 226 and 227: Rapitest Meters Garden Guide Soil T
- Page 228 and 229: Irrometer ® Soil Moisture Indicato
- Page 230 and 231: Digital Microscopes MicroSpin 2 MP
- Page 232 and 233: Compound Microscopes compound micro
- Page 234 and 235: Tubular Soil Sampler Soil Profile S
- Page 236 and 237: Mycorrhizal Applications is a leade
- Page 238 and 239: Fertilizers ARBORChar is uniquely b
- Page 240 and 241: HOLDS 200 TIMES ITS WEIGHT IN WATER
- Page 242 and 243: SUFFUSION® - Wetting, Penetrating,
- Page 244 and 245: Amendments, Soil Conditioners & Gro
- Page 246 and 247: HUMIC SOLUTIONS The Next Generation
- Page 248 and 249: Amendments, Soil Conditioners & Gro
- Page 250 and 251: terra char & other soil nutrients (
- Page 252 and 253: professional growing media Mycorrhi
- Page 254 and 255: Amendments, Soil Conditioners & Gro
- Page 256 and 257: Professional Growing Media Biofungi
- Page 258 and 259: Professional Growing Media Pro-Mix
- Page 260 and 261: Professional Growing Media High qua
- Page 262 and 263: Professional Growing Media Over the
- Page 264 and 265: ® Professional Growing Media The B
- Page 266 and 267: Premium Pro-mix premium products Po
- Page 268 and 269:
Baccto Potting Soil • Dark reed s
- Page 270 and 271:
GLOBAL LEADERS IN COCONUT COIR PROD
- Page 272 and 273:
Instant Green Soil Toppers supermos
- Page 274 and 275:
Oasis ® Wedge ® Growing Medium &
- Page 276 and 277:
Rockwool Rockwool • Proven to be
- Page 278 and 279:
Propagation Trays plastic liners
- Page 280 and 281:
• Easy to handle — saves time a
- Page 282 and 283:
Treepots treepots • trays Unique,
- Page 284 and 285:
QuickPot Propagation Trays HerkuPla
- Page 286 and 287:
SureRoots ® SureRoots ® 720720C 1
- Page 288 and 289:
T.O.P. propagation trays Propagatio
- Page 290 and 291:
Standard Inserts 1800 Series 1801 1
- Page 292 and 293:
T.O.P. specialty trays • pots •
- Page 294 and 295:
T.O.P. pots • carry trays • T.O
- Page 296 and 297:
Nu Pots & Nu Trays Nu-Tray 3-32 Nu-
- Page 298 and 299:
TEKU Thermoform Round Pots VCC21
- Page 300 and 301:
Specialty Perennial & Annual Pots I
- Page 302 and 303:
Hanging Baskets, Planters & Hangers
- Page 304 and 305:
Professional Grower Products Progro
- Page 306 and 307:
Coco Fiber Lined Hanging Baskets
- Page 308 and 309:
Wood Woven Baskets SuperMoss Natura
- Page 310 and 311:
Whether grown as a hanging basket o
- Page 312 and 313:
Grip- Lip The Grip-Lip is the late
- Page 314 and 315:
grow-tubs • container silks Gro-T
- Page 316 and 317:
TM Horticulture Growing Containers
- Page 318 and 319:
Plant, Rooting & Watering Trays Low
- Page 320 and 321:
Hydroponic Trays & Growing Trays
- Page 322 and 323:
Designed and Manufactured for Stren
- Page 324 and 325:
Fiber Clay Pots Austram’s new fib
- Page 326 and 327:
Plastic Vases & Pots Teraplast plas
- Page 328 and 329:
ITML pots, bowls, & saucers Panterr
- Page 330 and 331:
• Made of durable waterproof resi
- Page 332 and 333:
Terrazzo Heavy Duty Planters • Th
- Page 334 and 335:
Transparent Display & Growing Conta
- Page 336 and 337:
“So Real” Performance Planters
- Page 338 and 339:
Clear Vinyl Saucers • Made of cle
- Page 340 and 341:
Better Than Rocks Hummert’s Corr
- Page 342 and 343:
Easy to make and even easier to mai
- Page 344 and 345:
Decorative Soil Covers Mosser Lee D
- Page 346 and 347:
Fairy Gardens Collection Any area i
- Page 348 and 349:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) -
- Page 350 and 351:
Akro-Mills 365 Garden Products An i
- Page 352 and 353:
SpinNet Watering & Sprinkling Nozzl
- Page 354 and 355:
VibroNet Misting Nozzles Netafim mi
- Page 356 and 357:
Misting & Watering Nozzles PIN PERF
- Page 358 and 359:
misting nozzles Inverted Misting No
- Page 360 and 361:
Pressure Compensating (PC) Twist We
- Page 362 and 363:
Tape-Loc Fittings For use with all
- Page 364 and 365:
Landscape Techline ® HCVXR Driplin
- Page 366 and 367:
Multi-Outlet Dripper (MOD) Solution
- Page 368 and 369:
Dribble Tubes The SlimWeight is ma
- Page 370 and 371:
Spot-Spitters ® The Spot-Spitter
- Page 372 and 373:
Polyethylene Tubing & Fittings poly
- Page 374 and 375:
Oetiker One-Ear And Two-Ear Clamps
- Page 376 and 377:
power-loc TM fittings Power-Loc TM
- Page 378 and 379:
Male x Male Brass Fittings Female x
- Page 380 and 381:
Filters Disc Filters Disc filters o
- Page 382 and 383:
water treatment & filtration Health
- Page 384 and 385:
Grower Capillary Mats Unique, one-o
- Page 386 and 387:
trident controller The Highly Versa
- Page 388 and 389:
Super TM Nova 12 Zone Misting Contr
- Page 390 and 391:
Misting & Watering Controllers Wate
- Page 392 and 393:
Misting & Watering Controllers mist
- Page 394 and 395:
Remote Control Watering Controller
- Page 396 and 397:
GalPro is available in a battery op
- Page 398 and 399:
Program Repeating Timer This is one
- Page 400 and 401:
solenoid valves S Heavy-duty Hunter
- Page 402 and 403:
Irrigation & Watering Tools Irrigat
- Page 404 and 405:
Watering Wands 8 Pattern Long Neck
- Page 406 and 407:
Watering Nozzles watering nozzles S
- Page 408 and 409:
Watering & Spray Nozzles Adjustable
- Page 410 and 411:
Hose Accessories Quarter Turn Brass
- Page 412 and 413:
Hose Accessories quick connectors G
- Page 414 and 415:
FLEXZILLA SwivelGrip Garden Hose A
- Page 416 and 417:
• Extreme all-weather flexibility
- Page 418 and 419:
Colorite Premium Watering Hose Maxl
- Page 420 and 421:
Polyurethane Garden Hose Benefits a
- Page 422 and 423:
Watering Products watering hose men
- Page 424 and 425:
2-Ear Clamps Brass Couplings with H
- Page 426 and 427:
Heavy Duty Hose Reels • These hea
- Page 428 and 429:
hose menders & couplers hose hanger
- Page 430 and 431:
Oscillating Sprinklers Large Oscill
- Page 432 and 433:
Sprinkler Heads & Sprinklers sprink
- Page 434 and 435:
Model WM-12 Standard Attachments Wa
- Page 436 and 437:
A better way to water foliage plant
- Page 438 and 439:
Hydroponic Growing Systems AmHYDRO
- Page 440 and 441:
The Sustainable Solution - A comple
- Page 442 and 443:
Aeroponic Systems By generating a f
- Page 444 and 445:
Hydroponic Trays & Growing Trays
- Page 446 and 447:
2” Net Cup Net Pots 3” Net Cup
- Page 448 and 449:
Oxygen Infusion oxygen infusers •
- Page 450 and 451:
clay pebbles • garden tower 2 •
- Page 452 and 453:
Greenhouse Design Questionnaire Tak
- Page 454 and 455:
SL Series GREENHOUSES Ludy Greenhou
- Page 456 and 457:
EZ-Up Direct GREENHOUSES The Ludy E
- Page 458 and 459:
ABLE 7500 Conley’s Gable Series 7
- Page 460 and 461:
UPERSTAR 3000 Conley’s Superstar
- Page 462 and 463:
Florian greenhouses Florian’s Gen
- Page 464 and 465:
The Matterhorn Lean-To greenhouse i
- Page 466 and 467:
Hummert’s High Tunnels Approved F
- Page 468 and 469:
OLD FRAME Conley’s CF Series are
- Page 470 and 471:
Seasonal Retail Greenhouses Garden
- Page 472 and 473:
Pedestrian & Equipment Doors Overhe
- Page 474 and 475:
LEXAN THERMOCLEAR 15 LEXAN THERMOCL
- Page 476 and 477:
LEXAN Greca Corrugated Sheet & VERO
- Page 478 and 479:
Twin-Wall Flexible Covering Panels
- Page 480 and 481:
GREENHOUSES Greenhouse Glazing Extr
- Page 482 and 483:
fasteners Self Drilling TEK Screws
- Page 484 and 485:
Since 1924, Warp Brothers have been
- Page 486 and 487:
Sunview ® Greenhouse Films Poly-AG
- Page 488 and 489:
Polydress® SolaWrap is a flexible
- Page 490 and 491:
Polyethylene Film Accessories polye
- Page 492 and 493:
Energy Curtains PowerPull Energy Cu
- Page 494 and 495:
Environmental Screens Our business
- Page 496 and 497:
Coverings & Accessories Americover
- Page 498 and 499:
Aluminet ® Shade Cloth Aluminet®
- Page 500 and 501:
Bulk Knitted Shade Fabric • 60% B
- Page 502 and 503:
Insect Screen Support Systems Insta
- Page 504 and 505:
Pest & Predator Screens Pollination
- Page 506 and 507:
Greenhouse Benches Made in the USA
- Page 508 and 509:
Hi-low Light Mobile Bench Adjustabl
- Page 510 and 511:
A-V Bench Systems A-V Bench Systems
- Page 512 and 513:
Multi-Level Tables • Any configur
- Page 514 and 515:
“A” Frame Benches Made in the U
- Page 516 and 517:
Work Tables Made in the USA These i
- Page 518 and 519:
Vent & Curtain Drive Systems STRONG
- Page 520 and 521:
Natural Ventilation Systems If you
- Page 522 and 523:
Wall Shutters & Propeller Fans Alum
- Page 524 and 525:
Exhaust Fans MAL - Aluminum Exhaust
- Page 526 and 527:
The Leader In Light Traps Breathabl
- Page 528 and 529:
Rough Opening for GSWH & SWHA Housi
- Page 530 and 531:
AME HAF Fans AME/HAF fans • V-flo
- Page 532 and 533:
Air Distribution System The Fan-Jet
- Page 534 and 535:
Indoor Dehumidifiers Expand growing
- Page 536 and 537:
Odor Neutralizing System odor contr
- Page 538 and 539:
KOOL-CEL with Extruded Gutter KOOL-
- Page 540 and 541:
Evaporative Cooling Systems To coun
- Page 542 and 543:
Evaporative Cooling Water Treatment
- Page 544 and 545:
Evaporative Air Coolers Champion ev
- Page 546 and 547:
Gas-Fired Unit Heaters Horizontal P
- Page 548 and 549:
Electric Unit Heaters Horizontal De
- Page 550 and 551:
Efficient Greenhouse Heating BioThe
- Page 552 and 553:
Atomizing Humidifier Model 707-U
- Page 554 and 555:
® Leader in Automated Control Syst
- Page 556 and 557:
WADSWORTH C ontrol S yste ms Wadswo
- Page 558 and 559:
MICRO GROW GREENHOUSE SYSTEMS, INC.
- Page 560 and 561:
Greenhouse Controllers LinkConn Sof
- Page 562 and 563:
Bartlett Greenhouse Controllers Bar
- Page 564 and 565:
alarm systems & thermostats The Ala
- Page 566 and 567:
HortiLED The Future of Grow Lightin
- Page 568 and 569:
LED Grow Lights The Future of Indoo
- Page 570 and 571:
LED Grow Lights & Bulbs TotalGrow S
- Page 572 and 573:
PLX Magnetic Ballasts P.L. light PL
- Page 574 and 575:
light meters • HPS/LED safety gla
- Page 576 and 577:
Sun Blaze T5 Fixtures Plant Light 4
- Page 578 and 579:
Flora Cart Flora & Lite Carts BA3 M
- Page 580 and 581:
Grow Tents 3’ x 3’ x 6’11”
- Page 582 and 583:
G-Floor Growfloor Growfloor is a pr
- Page 584 and 585:
Berry Value-Line Production Seeder
- Page 586 and 587:
JP-1 Jang Hand Seeder by Mechanical
- Page 588 and 589:
Dibble Pro Dibble Mate Dibble Pro
- Page 590 and 591:
Heat Mats & Controllers heat mats &
- Page 592 and 593:
Mobile Growing Bench The Hummert Mo
- Page 594 and 595:
Soil & Belt Conveyors Soil Conveyor
- Page 596 and 597:
Hummert’s Media Steamer Carts Des
- Page 598 and 599:
Hummert’s A-Z Pre-Fab Steam Struc
- Page 600 and 601:
Rain Gauges rain gauges Copper Stak
- Page 602 and 603:
Thermometers & Hygrometers thermome
- Page 604 and 605:
hygrometers • weather meters Maso
- Page 606 and 607:
Wireless Weather Stations Davis wir
- Page 608 and 609:
field management • environment re
- Page 610 and 611:
Plastic Mulch Layers Rain-Flo plast
- Page 612 and 613:
Challenger Plastic Mulch Lifter Hor
- Page 614 and 615:
Raised Beds LGarden Original Design
- Page 616 and 617:
Portable Patio Garden Love to garde
- Page 618 and 619:
All-Season Plant Protection All our
- Page 620 and 621:
Flat Cold Frames flat cold frames
- Page 622 and 623:
Mantis Deluxe 4-Cycle Tiller All Ma
- Page 624 and 625:
BCS Tiller Attachments Rear Tine Ti
- Page 626 and 627:
Frost Protection Fabric N-sulate TM
- Page 628 and 629:
plant protector • fruit picker
- Page 630 and 631:
MACXAce Vented Bins Fruit & Vegetab
- Page 632 and 633:
Fruit & Vegetable Containers & Pack
- Page 634 and 635:
Bamboo Stakes These superior stakes
- Page 636 and 637:
Plant Supports & Products Pot Hange
- Page 638 and 639:
trellises • plant ties/string 36
- Page 640 and 641:
twine • clips Twine Cotton Beacon
- Page 642 and 643:
plant lok • ties Quick-Tys • QU
- Page 644 and 645:
Support Accessories 1117 1110 1107
- Page 646 and 647:
BJA Tape Binders TOMATOES TOMATOES
- Page 648 and 649:
plastic labels Plastic Labels White
- Page 650 and 651:
Plastic Labels BT5 BT6 BAU White St
- Page 652 and 653:
Garden Labels & Stakes Push-On Plan
- Page 654 and 655:
Impress-O-Tag •Ties attached •
- Page 656 and 657:
labels • pennant flags Nursery Ma
- Page 658 and 659:
Allflex Horticultural Pen RESISTS F
- Page 660 and 661:
Plastic Measuring Wheels Make Your
- Page 662 and 663:
Hummert's ® SUPER SCOOP In Neon Hu
- Page 664 and 665:
Pruners & Scissors Fiskars pruners
- Page 666 and 667:
Corona Pruners Bypass Pruner BP6250
- Page 668 and 669:
Felco Pruners F2 F4 F5 Solidly forg
- Page 670 and 671:
Colorpoint Cutting Tools • Each o
- Page 672 and 673:
Professional Pruners & Shears Bypas
- Page 674 and 675:
Hedge Shears Model HS 6920 • Drop
- Page 676 and 677:
Commercial Tree Pruners & Pole Saws
- Page 678 and 679:
Telescoping Pruners • Perfectly b
- Page 680 and 681:
Pruning Saws Fixed Blade Saws Heavy
- Page 682 and 683:
Corona Extendable Handle Garden Too
- Page 684 and 685:
Knives & Tools For the Horticulturi
- Page 686 and 687:
Bushcraft is about getting to know
- Page 688 and 689:
Shovels & Scoops D A B C F E AMES g
- Page 690 and 691:
Rakes & Forks A B D E F G H I J AME
- Page 692 and 693:
E-Z Reacher ® Pick-Up Tool All-Ste
- Page 694 and 695:
The Seed Stitcher is a revolutionar
- Page 696 and 697:
Cotton - Polyester Aprons Full leng
- Page 698 and 699:
Model 7733 • Heavyweight suede co
- Page 700 and 701:
knee pads Professional Kneepads Mod
- Page 702 and 703:
Gorilla Tubs Plastic Hand Baskets L
- Page 704 and 705:
Garden Center Carts 2-Wheel Push Ca
- Page 706 and 707:
Nursery 2-Wheelers Designed to make
- Page 708 and 709:
Garden Carts Hummert’s garden •
- Page 710 and 711:
Storage Cabinets • Engineered for
- Page 712 and 713:
Garden Center Carts • It is a kno
- Page 714 and 715:
Heavy Duty Tilt Trucks 5/8 Cubic Ya
- Page 716 and 717:
Wheelbarrows & Carts 3.5 Bushel Ope
- Page 718 and 719:
Traction Drive Platform Cart • Id
- Page 720 and 721:
Concrete & Stone Cutter Trimmers Tr
- Page 722 and 723:
Trimmers PAS-266 - Pro Attachment S
- Page 724 and 725:
Mowers • Heavy-duty steel cutting
- Page 726 and 727:
Blowers Echo Hand Held Blower PB-25
- Page 728 and 729:
BLOW IT SHRED IT BAG IT Model ES250
- Page 730 and 731:
Hedge Trimmers - Double Sided Blade
- Page 732 and 733:
Solid, welded construction, strong
- Page 734 and 735:
SG340 Stump Grinder stump grinder
- Page 736 and 737:
protection products Forestry Protec
- Page 738 and 739:
Grafting Tools Both tools give exac
- Page 740 and 741:
How It Works Saving time and labor,
- Page 742 and 743:
Tree Anchoring Accessories Agricult
- Page 744 and 745:
tree straps • ties Prolock Poly C
- Page 746 and 747:
CoCo Weed Mats • Keeps moisture i
- Page 748 and 749:
Ground Cover Sunbelt Woven Ground C
- Page 750 and 751:
Erosion Control Erosion Control Bla
- Page 752 and 753:
Black Diamond The landscape industr
- Page 754 and 755:
Professional Edging Designed with a
- Page 756 and 757:
Ez-Roll Permeable Pavers Ez-Roll pa
- Page 758 and 759:
Dyna Green grass seed Dyna Green TM
- Page 760 and 761:
How to Read an Analysis Tag Lot # E
- Page 762 and 763:
Decorative Mulch Cocoa Shells • M
- Page 764 and 765:
Magnetic Drive Hybrid Pumps Fountai
- Page 766 and 767:
• Easy to bait, set, and release
- Page 768 and 769:
Deer & Rabbit Repellent • Stop an
- Page 770 and 771:
Gopher, Mole & Vole Controls Gopher
- Page 772 and 773:
Gopher & Mole Traps gopher, mole &
- Page 774 and 775:
Spring Action Snap Traps Rodent Con
- Page 776 and 777:
Mosquito Control Products mosquito
- Page 778 and 779:
turf products & coco disks beetle t
- Page 780 and 781:
Decorative Soil Covers Mosser Lee D
- Page 782 and 783:
Floral Supplies Sheet Moss Natural
- Page 784 and 785:
Powers Flower Coolers Standard feat
- Page 786 and 787:
Alumagoal 4-Wheel, 100 lb Field Cha
- Page 788 and 789:
de-icing products Calcium Chloride
- Page 790 and 791:
Cardinal & Songbird Food Premium Wi
- Page 792 and 793:
Product Display Cases Available dis
- Page 794 and 795:
Product Displays Since 1941, Dramm
- Page 796 and 797:
product displays Page’s Seeds Dis
- Page 798 and 799:
Assorted Fertilizers & Lawn Seed Yo
- Page 800 and 801:
Garden Product Displays garden prod
- Page 802 and 803:
Hummert spring & fall bulbs 800 800
- Page 804 and 805:
Merchandise Display Shelving Let SP
- Page 806 and 807:
Truck Shipments Hummert Internation
- Page 808 and 809:
4500 Earth City Expwy. 314-506-4500
- Page 810 and 811:
Terms & Conditions of Sale Ordering
- Page 812 and 813:
Index of Our 2018-2019 Catalog inde
- Page 814 and 815:
Index of Our 2018-2019 Catalog Fung
- Page 816 and 817:
Index of Our 2018-2019 Catalog inde
- Page 818 and 819:
Index of Our 2018-2019 Catalog inde
- Page 820:
4500 Earth City Expressway Earth Ci