part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
part 1: overview of cogeneration and its status in asia - Fire
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
110 Part3: Summary <strong>of</strong> country studies – Bangladesh <strong>and</strong> Viet Nam<br />
Excess(+)/Deficit(-) Power, MWh/year -1,480 5,485<br />
Fuel Consumption, TJ/year 116 187<br />
Gas Turb<strong>in</strong>e<br />
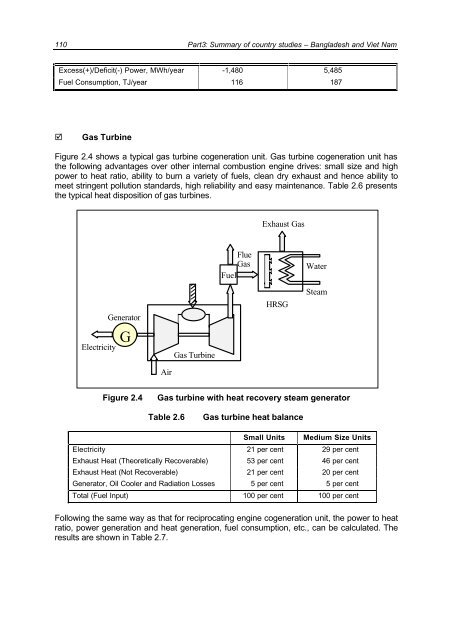
Figure 2.4 shows a typical gas turb<strong>in</strong>e <strong>cogeneration</strong> unit. Gas turb<strong>in</strong>e <strong>cogeneration</strong> unit has<br />
the follow<strong>in</strong>g advantages over other <strong>in</strong>ternal combustion eng<strong>in</strong>e drives: small size <strong>and</strong> high<br />
power to heat ratio, ability to burn a variety <strong>of</strong> fuels, clean dry exhaust <strong>and</strong> hence ability to<br />
meet str<strong>in</strong>gent pollution st<strong>and</strong>ards, high reliability <strong>and</strong> easy ma<strong>in</strong>tenance. Table 2.6 presents<br />
the typical heat disposition <strong>of</strong> gas turb<strong>in</strong>es.<br />
Electricity<br />
Generator<br />
G<br />
Air<br />
Gas Turb<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Flue<br />
Gas<br />
Fuel<br />
Exhaust Gas<br />
HRSG<br />
Figure 2.4 Gas turb<strong>in</strong>e with heat recovery steam generator<br />
Table 2.6 Gas turb<strong>in</strong>e heat balance<br />
Water<br />
Steam<br />
Small Un<strong>its</strong> Medium Size Un<strong>its</strong><br />
Electricity 21 per cent 29 per cent<br />
Exhaust Heat (Theoretically Recoverable) 53 per cent 46 per cent<br />
Exhaust Heat (Not Recoverable) 21 per cent 20 per cent<br />
Generator, Oil Cooler <strong>and</strong> Radiation Losses 5 per cent 5 per cent<br />
Total (Fuel Input) 100 per cent 100 per cent<br />
Follow<strong>in</strong>g the same way as that for reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>e <strong>cogeneration</strong> unit, the power to heat<br />
ratio, power generation <strong>and</strong> heat generation, fuel consumption, etc., can be calculated. The<br />
results are shown <strong>in</strong> Table 2.7.